Key Takeaways
- L-Carnitine supports fat metabolism and energy production.
- Benefits include enhanced exercise performance and improved heart health.
- Proper dosing minimizes potential side effects.
Understanding L-Carnitine
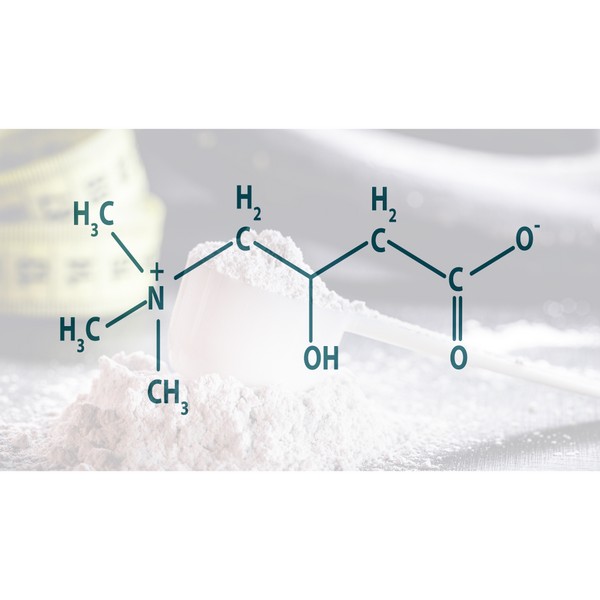
L-Carnitine, derived from amino acids, is essential for energy production. It transports long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized to produce energy.
This process is vital for muscle function and various other body systems.
Benefits of L-Carnitine

Enhancing Fat Metabolism
L-Carnitine facilitates fat breakdown, aiding in weight management. Improved fat oxidation converts stored fat into usable energy, which is particularly beneficial during exercise.
Enhanced fat metabolism supports overall health and energy levels.
Boosting Energy Levels
L-Carnitine plays a key role in mitochondrial energy production. Transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria ensures efficient energy generation.
This boost in energy levels can improve physical performance and reduce fatigue during intense activities.
Supporting Heart Health
L-Carnitine positively impacts cardiovascular health. It helps reduce risk factors for heart disease, such as high cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
Improved heart health supports overall wellness and longevity.
Improving Exercise Performance
Increased endurance and quicker recovery are significant benefits of L-Carnitine supplementation. It reduces muscle damage and fatigue, allowing for more intense and prolonged workouts.
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts often use L-Carnitine to enhance their training results.
Natural Sources of L-Carnitine

Foods Rich in L-Carnitine
Red meat, especially beef, is one of the best sources of L-Carnitine. Fish, poultry, and dairy products also provide significant amounts.
Including these foods in your diet ensures a steady supply of L-Carnitine. These foods not only provide L-Carnitine but also offer essential nutrients needed for optimal body function.
For those following a vegetarian or vegan diet, supplementation becomes more important as plant-based sources are limited.
Dosage Recommendations
Suggested Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake of L-Carnitine typically ranges from 500 to 2000 mg. This dosage can vary based on individual health conditions and activity levels.
Timing and Method of Supplementation
L-Carnitine should be taken with meals to enhance absorption. Splitting the daily dose into smaller amounts helps maintain steady levels in the body.
Taking it before workouts maximizes its benefits for exercise performance.
Variations Based on Individual Needs
Athletes and those engaged in high-intensity training might require higher doses. People with specific health conditions, like cardiovascular issues or chronic fatigue, should consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage.
Who Should Consider L-Carnitine Supplementation?

Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts
Athletes looking to improve performance and endurance will benefit from L-Carnitine. It is particularly effective for those involved in high-intensity sports and training.
Individuals Aiming for Weight Management
People aiming to manage their weight find L-Carnitine useful for enhancing fat metabolism. Its ability to convert stored fat into energy supports weight loss efforts.
Those with Specific Health Conditions
Individuals with cardiovascular issues or chronic fatigue may benefit from L-Carnitine supplementation. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures safe and appropriate use.
Potential Side Effects

L-Carnitine is generally safe, but some individuals might experience mild digestive issues. These can include nausea, stomach cramps, and diarrhea.
Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize these side effects.
Long-term Use
Research indicates that long-term use of L-Carnitine is safe. Adhering to recommended dosages avoids potential risks.
Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider ensures safe and effective long-term use.
Interactions with Other Supplements
Combining L-Carnitine with other supplements can enhance its benefits. For example, pairing it with Omega-3 fatty acids can support cardiovascular health.
Being aware of potential contraindications is necessary. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen is advisable.
Conclusion
L-Carnitine supports fat metabolism, boosts energy levels, enhances exercise performance, and promotes heart health. Understanding proper dosage and potential side effects ensures safe and effective use.
FAQs
What is L-Carnitine?
L-Carnitine is a compound that plays a key role in fat metabolism and energy production. It is derived from amino acids and is vital for transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria.
How does L-Carnitine improve exercise performance?
L-Carnitine enhances endurance, aids in recovery, and reduces muscle damage and fatigue. It helps transport fatty acids into the mitochondria, boosting energy production during exercise.
What are the common side effects of L-Carnitine?
Common side effects include mild digestive issues such as nausea, stomach cramps, and diarrhea. These can often be minimized by starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it.
How much L-Carnitine should I take daily?
The recommended dosage typically ranges from 500 to 2000 mg per day. Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized advice ensures safe and effective use.
Which foods are high in L-Carnitine?
Foods such as red meat, fish, poultry, and dairy products are rich in L-Carnitine. These sources help maintain adequate levels naturally, supporting muscle function and overall health.
Who can benefit from L-Carnitine supplementation?
Athletes, fitness enthusiasts, individuals aiming for weight management, and those with specific health conditions like cardiovascular issues may benefit from L-Carnitine. Consulting a healthcare provider before starting supplementation is recommended.
Research
Brass, E.P., 1995. Pharmacokinetic considerations for the therapeutic use of carnitine in hemodialysis patients. Clinical therapeutics, 17(2), pp.176-185.
Fielding, R., Riede, L., Lugo, J.P., & Bellamine, A., 2018. L-Carnitine Supplementation in Recovery after Exercise. Nutrients, 10(3), 349.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030349
Fritz, I.B., 1959. Action of carnitine on long chain fatty acid oxidation by liver. American Journal of Physiology-Legacy Content, 197(2), pp.297-304.
Iyer, R.N., Khan, A.A., Gupta, A., Vajifdar, B.U. and Lokhandwala, Y.Y., 2000. L-carnitine moderately improves the exercise tolerance in chronic stable angina. The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 48(11), pp.1050-1052.
Karlic, H., & Lohninger, A., 2004. Supplementation of L-carnitine in athletes: does it make sense? Nutrition, 20(7-8), 709-715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2004.04.003
Novakova K, Kummer O, Bouitbir J, Stoffel SD, Hoerler-Koerner U, Bodmer M, Roberts P, Urwyler A, Ehrsam R, Krähenbühl S. Effect of L-carnitine supplementation on the body carnitine pool, skeletal muscle energy metabolism and physical performance in male vegetarians. Eur J Nutr. 2016 Feb;55(1):207-17. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0838-9. Epub 2015 Jan 23. PMID: 25612929.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25612929/
Rigault, C., Mazué, F., Bernard, A., Demarquoy, J. and Le Borgne, F., 2008. Changes in L-carnitine content of fish and meat during domestic cooking. Meat science, 78(3), pp.331-335.
Sawicka, A.K., Renzi, G. and Olek, R.A., 2020. The bright and the dark sides of L-carnitine supplementation: a systematic review. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 17, pp.1-10.
Tanphaichitr V, Leelahagul P. Carnitine metabolism and human carnitine deficiency. Nutrition. 1993 May-Jun;9(3):246-54. PMID: 8353366.
L-Carnitine: Benefits, Dosage, and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Carnitine supports fat metabolism and energy production. Benefits include enhanced exercise performance and improved heart health. Proper dosing minimizes potential side effects. Understanding…
TUDCA Benefits for Health
Key Takeaways TUDCA promotes liver health, aiding cell protection and repair. Enhances digestion by improving bile flow and supporting gut health. May protect brain health…
Vitamin E Complex
Key Takeaways Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. The vitamin E complex includes…
Berberine Has 11 More Incredible Benefits Than You Thought
Berberine is a compound found in several plants that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda. It has recently gained popularity…
Trimethylglycine TMG: Betaine Anhydrous Explained
Key Takeaways Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) is a compound found naturally in various foods and offers several health benefits. TMG supports liver health by reducing fatty…
Creatine Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways Common myths about creatine, such as it causing kidney damage, weight gain, and being a steroid, are widespread but unsupported by scientific evidence….
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA): Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways CLA is a type of fatty acid found primarily in animal products like beef and dairy. Known for potential benefits such as weight…
Taurine: The Mighty Amino Acid for Optimal Health
Key Takeaways Taurine supports heart health, regulates blood pressure, and reduces oxidative stress. Essential for muscle function, brain health, and cognitive function. Aids in insulin…
L-Glutamine and Gut Health: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Glutamine is essential for gut health. Benefits include improved digestion and reduced inflammation. Potential side effects are rare but can occur in high…
Postbiotics: What They Are and Why They Are Important
Key Takeaways Postbiotics 101: They’re beneficial by-products from probiotics that consume prebiotics Boosts Immunity: Postbiotics sharpen your immune system, helping fight off pathogens and reducing…
Spirulina: Health Benefits and Uses
Key Takeaways Spirulina boosts immune function with its high nutrient content and antioxidant properties. Rich in proteins and essential vitamins, enhances overall nutrition. Helps reduce…
Medium Chain Triglycerides (MCTs): Uncovering 5 Health Benefits
This potent, natural source of energy has gained considerable attention in recent years for its impressive array of benefits. MCT oil is a versatile addition…