Key Takeaways
- NAFLD involves fat buildup in the liver not caused by alcohol.
- Commonly associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
- NAFLD can lead to severe liver conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis if untreated.
- Diet rich in nutrient-dense foods, along with regular physical activity, is key to managing and preventing NAFLD.
- Early detection and intervention are important to prevent progression to more serious liver diseases.
What is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
Definition of NAFLD
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat buildup in the liver cells, accounting for more than 5-10% of the liver’s weight, without significant alcohol consumption.
It is increasingly common, particularly in people who are overweight, have type 2 diabetes, or suffer from metabolic syndrome.
NAFLD can progress from simple fat accumulation in the liver to more severe conditions that damage liver function.
Stages of NAFLD
- Simple Fatty Liver (Steatosis): This stage involves the accumulation of fat in the liver cells without significant inflammation or liver damage.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): This more advanced stage is marked by liver inflammation and cell damage, which can lead to fibrosis (scarring) of the liver.
- Fibrosis and Cirrhosis: Prolonged inflammation and liver damage can result in fibrosis and, eventually, cirrhosis, which significantly impairs liver function and may lead to liver failure.
Causes and Risk Factors

Obesity and Overweight
Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, is strongly linked to NAFLD. Obesity increases the likelihood of fat being deposited in the liver.
Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin resistance, commonly seen in type 2 diabetes, promotes fat accumulation in the liver and is a major risk factor for NAFLD.
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome, which includes conditions such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels, significantly increases the risk of developing NAFLD.
Genetic Factors
Genetics may also influence the development of NAFLD, making some individuals more susceptible to the condition.
Poor Diet and Sedentary Lifestyle
A diet high in carbohydrates and ultra-processed foods, combined with a lack of physical activity, contributes to fat buildup in the liver.
Fructose, especially from high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), contributes significantly to the development of NAFLD by promoting de novo lipogenesis (DNL) and increasing triglyceride accumulation in the liver.
Unlike glucose, fructose metabolism bypasses key regulatory steps, leading to rapid fat synthesis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory responses in the liver.
Excessive fructose intake is linked to the progression of liver damage, including fibrosis, through mechanisms involving increased uric acid levels, ATP depletion, and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Symptoms of NAFLD
Early Stages (Steatosis)
NAFLD often does not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Many individuals with simple fatty liver are unaware they have the condition.
Advanced Stages (NASH and Cirrhosis)
As NAFLD progresses, symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, weight loss, and discomfort in the upper right abdomen.
Advanced liver damage can lead to jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), swelling in the abdomen and legs, and mental confusion.
Diagnosis of NAFLD
Blood Tests (Liver Enzymes)
Elevated liver enzyme levels in blood tests can indicate liver inflammation or damage, which may suggest the presence of NAFLD.
Imaging Tests (Ultrasound, MRI)
Imaging tests like ultrasounds or MRIs can detect fat accumulation in the liver, helping to confirm a diagnosis of NAFLD.
Liver Biopsy
In some cases, a liver biopsy might be needed to determine the extent of liver damage and to distinguish between simple fatty liver and NASH.
Treatment and Management of NAFLD

Lifestyle Changes
Diet:
- Avoid grains, sugars, and processed foods, which contribute to liver fat accumulation.
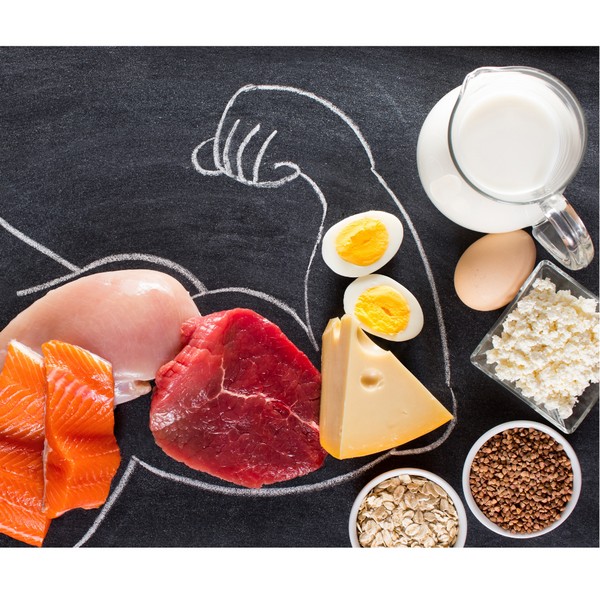
- Emphasize a diet rich in bio-available foods, such as grass-fed ruminant red meat and organs, pasture-raised eggs, and wild-caught seafood.
- Include healthy animal fats like ghee, butter, and tallow.
Exercise:
- Regular physical activity is important.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to help reduce liver fat and improve overall metabolic health.
Weight Loss:
- Gradual and sustained weight loss can significantly reduce liver fat and inflammation, lowering the risk of progression to more severe liver disease.
Medications and Medical Interventions
Currently, there are no specific medications approved for treating NAFLD. However, managing conditions like diabetes, and insulin resistance may help reduce the risk of liver damage.
Lifestyle changes remain the most effective treatment.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring of liver function through blood tests and imaging is essential for tracking the progression of NAFLD and adjusting treatment as needed.
Prevention of NAFLD

Healthy Diet
A diet focused on bioavailable nutrient-dense whole foods while avoiding grains, sugars, and ultra-processed foods can help prevent the development of NAFLD.
Regular Physical Activity
Maintaining a regular exercise routine helps prevent fat buildup in the liver and supports overall health.
Weight Management
Keeping a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise is key to preventing NAFLD.
Potential Complications
Progression to NASH
If left untreated, simple fatty liver can progress to NASH, leading to more severe liver inflammation and damage.
Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver inflammation can lead to fibrosis (scarring) and eventually cirrhosis, which severely impairs liver function and can lead to liver failure.
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
NAFLD is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases due to its links with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
Conclusion
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is a common but potentially serious condition that can progress to severe liver damage if not managed properly. A diet rich in animal-based foods, combined with regular physical activity and weight management, is the most effective way to treat and prevent NAFLD. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical to preventing the progression to more serious liver conditions.
FAQs
What causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
NAFLD is primarily caused by obesity, insulin resistance, and poor dietary habits, leading to fat accumulation in the liver.
Can NAFLD be reversed?
Yes, NAFLD can often be reversed through dietary changes, regular exercise, and sustained weight loss.
What is the difference between NAFLD and NASH?
NAFLD involves fat buildup in the liver, while NASH includes inflammation and liver cell damage, which can lead to more serious conditions like fibrosis and cirrhosis.
How is NAFLD diagnosed?
NAFLD is diagnosed through blood tests, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI, and sometimes a liver biopsy to assess the extent of liver damage.
What lifestyle changes can help manage NAFLD?
Adopting a diet rich in animal-based foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and achieving gradual weight loss are key to managing and preventing NAFLD.
Research
Ambreen, G., Siddiq, A., & Hussain, K. (2020). Association of long-term consumption of repeatedly heated mix vegetable oils in different doses and hepatic toxicity through fat accumulation. *Lipids in Health and Disease*, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-020-01256-0.
Anderson, E.L., Howe, L.D., Jones, H.E., Higgins, J.P.T., Lawlor, D.A., & Fraser, A. (2015). The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. *PLOS ONE*, 10(10), p.e0140908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140908.
Asrih, M., & Jornayvaz, F. R. (2014). Diets and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The good and the bad. Clinical Nutrition, 33(2), 186-190.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2013.11.003
Basaranoglu, M., Basaranoglu, G., Sabuncu, T., & Sentürk, H. (2013). Fructose as a key player in the development of fatty liver disease. *World Journal of Gastroenterology*, 19(8), 1166-1172. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1166.
Chen, H.L., Tsai, T.C., Tsai, Y.C., Liao, J.W., Yen, C.C., & Chen, C.M. (2016). Kefir peptides prevent high-fructose corn syrup-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a murine model by modulation of inflammation and the JAK2 signaling pathway. *Nutrition & Diabetes*, 6(12), pp.e237. https://doi.org/10.1038/nutd.2016.49.
Coronati, M., Baratta, F., Pastori, D., Ferro, D., Angelico, F., & Del Ben, M. (2022). Added fructose in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and in metabolic syndrome: A narrative review. *Nutrients*, 14(6), p.1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061127.
D’Abbondanza, M., Ministrini, S., Pucci, G., Nulli Migliola, E., Martorelli, E.-E., Gandolfo, V., Siepi, D., Lupattelli, G., & Vaudo, G. (2020). Very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet for the treatment of severe obesity and associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of sex differences. *Nutrients*, 12(9), p.2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092748.
D., J., P., A., & F., J. Different dietary approaches, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease: A literature review. *Nutrients*, 15(6), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061483.
Fan, G., & Cao, X. Role of diet and nutritional management in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. *Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology*, 28, 81-87. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12244.
Félix, D.R., Costenaro, F., Gottschall, C.B.A., & Coral, G.P. (2016). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in obese children—effect of refined carbohydrates in diet. *BMC Pediatrics*, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-016-0726-3.
Gopalakrishnan Ravikumar, N.P., Nallapeta, N.S., & Mahl, T. (2019). Risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with increased intake of high fructose corn syrup (HFCS): A systematic review. *American Journal of Gastroenterology*, 114(1), pp.S1615. https://doi.org/10.14309/01.ajg.0000601436.73048.30.
Goss, A.M., Dowla, S., Pendergrass, M., Ashraf, A., Bolding, M., Morrison, S., Amerson, A., Soleymani, T., & Gower, B. (2020). Effects of a carbohydrate‐restricted diet on hepatic lipid content in adolescents with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot, randomized trial. *Pediatric Obesity*, 15(7). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijpo.12630.
Grinshpan, L.S., Eilat-Adar, S., Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D., Kariv, R., Gillon-Keren, M., & Zelber-Sagi, S. (2024). Ultra-processed food consumption and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: A systematic review. *JHEP Reports*, 6(1), p.100964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100964.
Hägele, F.A., Enderle, J., Rimbach, G., & Bosy-Westphal, A. (2023). Ultra-processed food consumption and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—What are the proposed mechanisms? *Exploration of Digestive Diseases*, 1(1), pp.133-148. https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2023.00023.
Hydes, T., Alam, U., & Cuthbertson, D.J. (2021). The impact of macronutrient intake on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Too much fat, too much carbohydrate, or just too many calories? *Frontiers in Nutrition*, 8, 640557. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.640557.
Ivancovsky‐Wajcman, D., Fliss‐Isakov, N., Webb, M., Bentov, I., Shibolet, O., Kariv, R., & Zelber‐Sagi, S. (2021). Ultra‐processed food is associated with features of metabolic syndrome and non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. *Liver International*, 41(11), pp.2635–2645. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14996.
Jarvis, H., Craig, D., Barker, R., Spiers, G., Stow, D., Anstee, Q.M., & Hanratty, B. (2020). Metabolic risk factors and incident advanced liver disease in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based observational studies. *PLOS Medicine*, 17(4), p.e1003100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003100.
Keating, S. E., Hackett, D. A., George, J., & Johnson, N. A. (2012). Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. *Journal of Hepatology*, 57(1), 157-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.02.023.
Konieczna, J., Fiol, M., Colom, A., Ángel, M., Corella, D., Trinidad, M., Martínez, J. A., M., Á., Wärnberg, J., Vioque, J., Estruch, R., Rosa, M., Lapetra, J., Tur, J. A., Martín Sánchez, V., Pintó, X., Gaforio, J. J., Vidal, J., Vázquez, C., . . . Romaguera, D. (2022). Does consumption of ultra-processed foods matter for liver health? Prospective analysis among older adults with metabolic syndrome. *Nutrients*, 14(19), p.4142. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194142.
Liu, Z., Huang, H., Zeng, Y., Chen, Y., & Xu, C. (2022). Association between ultra-processed foods consumption and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based analysis of NHANES 2011–2018. *British Journal of Nutrition*, 130(6), pp.996–1004. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114522003956.
Luukkonen, P. K., Dufour, S., Lyu, K., Zhang, X., Hakkarainen, A., Lehtimäki, T. E., Cline, G. W., Petersen, K. F., & Shulman, G. I. (2020). Effect of a ketogenic diet on hepatic steatosis and hepatic mitochondrial metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. *Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences*, 117(13), 7347-7354. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1922344117.
Luukkonen, P. K., Hodson, L., & Moore, J. B. (2021). Dietary carbohydrates and fats in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. *Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology*, 18(11), 770-786. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00472-y.
Marchesini, G., Brizi, M., Morselli-Labate, A.M., Bianchi, G., Bugianesi, E., McCullough, A.J., Forlani, G., & Melchionda, N. (1999). Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. *The American Journal of Medicine*, 107(5), pp.450–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9343(99)00271-5.
Musso, G., Gambino, R., Tabibian, J.H., Ekstedt, M., Kechagias, S., Hamaguchi, M., Hultcrantz, R., Hagström, H., Yoon, S.K., Charatcharoenwitthaya, P., George, J., Barrera, F., Hafliðadóttir, S., Björnsson, E.S., Armstrong, M.J., Hopkins, L.J., Gao, X., Francque, S., Verrijken, A., Yilmaz, Y., Lindor, K.D., Charlton, M., Haring, R., Lerch, M.M., Rettig, R., Völzke, H., Ryu, S., Li, G., Wong, L.L., Machado, M., Cortez-Pinto, H., Yasui, K., & Cassader, M. (2014). Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. *PLoS Medicine*, 11(7), p.e1001680. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001680.
Ouyang, X., Cirillo, P., Sautin, Y., McCall, S., Bruchette, J. L., Diehl, A. M., Johnson, R. J., & Abdelmalek, M. F. (2008). Fructose consumption as a risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. *Journal of Hepatology*, 48(6), 993-999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2008.02.011.
Pai, S.A., Munshi, R.P., & Juvekar, A.R. (2019). Partially hydrogenated vegetable oil containing 5% trans fats when combined with fructose exacerbates obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. *Nutrire*, 45(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41110-019-0105-6.
Papadopoulos, G., Legaki, A.-I., Georgila, K., Vorkas, P., Giannousi, E., Stamatakis, G., Moustakas, I.I., Petrocheilou, M., Pyrina, I., Gercken, B., Kassi, E., Chavakis, T., Pateras, I.S., Panayotou, G., Gika, H., Samiotaki, M., Eliopoulos, A.G., & Chatzigeorgiou, A. (2023). Integrated omics analysis for characterization of the contribution of high fructose corn syrup to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obesity. *Metabolism*, 144, p.155552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155552.
Park, G., Jung, S., Wellen, K. E., & Jang, C. (2021). The interaction between the gut microbiota and dietary carbohydrates in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 53(5), 809-822.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-021-00614-x
Targher, G., Byrne, C.D., Lonardo, A., Zoppini, G., & Barbui, C. (2016). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. *Journal of Hepatology*, 65(3), pp.589–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.013.
Watanabe, M., Tozzi, R., Risi, R., Tuccinardi, D., Mariani, S., Basciani, S., Spera, G., Lubrano, C., & Gnessi, L. (2020). Beneficial effects of the ketogenic diet on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive review of the literature. Obesity Reviews, 21(8), e13024.
https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13024
Ye, Q., Zou, B., Yeo, Y.H., Li, J., Huang, D.Q., Wu, Y., Yang, H., Liu, C., Kam, L.Y., Tan, X.X.E., Chien, N., Trinh, S., Henry, L., Stave, C.D., Hosaka, T., Cheung, R.C., & Nguyen, M.H. (2020). Global prevalence, incidence, and outcomes of non-obese or lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. *The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology*, 5(8), pp.739–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(20)30077-7.
Yki-Järvinen, H. (2015). Nutritional modulation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. *Nutrients*, 7(11), pp.9127–9138. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7115454.
Zhang, S., Gan, S., Zhang, Q., Liu, L., Meng, G., Yao, Z., Wu, H., Gu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, T., Wang, X., Sun, S., Wang, X., Zhou, M., Jia, Q., Song, K., Qi, L., & Niu, K. (2021). Ultra-processed food consumption and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Tianjin Chronic Low-grade Systemic Inflammation and Health Cohort Study. *International Journal of Epidemiology*, 51(1), pp.237–249. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyab174.
Zhang, Y.-F., Qiao, W., Zhuang, J., Feng, H., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Association of ultra-processed food intake with severe non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective study of 143073 UK Biobank participants. *The Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging*, 28(10), p.100352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnha.2024.100352.
Zhao, L., Clay-Gilmour, A., Zhang, J., Zhang, X., & Steck, S. E. (2024). Higher ultra-processed food intake is associated with adverse liver outcomes: A prospective cohort study of UK Biobank participants. *The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition*, 119(1), 49-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.10.014.
Zhao, L., Zhang, X., Martinez Steele, E., Lo, C.-H., Zhang, F.F., & Zhang, X. (2023). Higher ultra-processed food intake was positively associated with odds of NAFLD in both US adolescents and adults: A national survey. *Hepatology Communications*, 7(9). https://doi.org/10.1097/hc9.0000000000000240.
Insulin Resistance: What It Is & How to Manage It
Key Takeaways Insulin resistance leads to high blood sugar when cells stop responding to insulin. Often connected to obesity, poor diet, and physical inactivity. Symptoms…
L-Glutamine and Gut Health: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Glutamine is essential for gut health. Benefits include improved digestion and reduced inflammation. Potential side effects are rare but can occur in high…
Proteolytic Enzymes and Heart Health: What the Research Shows
Your heart works tirelessly to pump blood throughout your body, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to your cells. However, factors like poor diet, stress, and…
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Key Takeaways NAFLD involves fat buildup in the liver not caused by alcohol. Commonly associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can lead…
Parkinson’s Disease : Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Key Takeaways Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement and coordination. Oxidative stress and excess iron are significant factors in the progression…
Boost Insulin Sensitivity Naturally
Key Takeaways Improving insulin sensitivity helps control blood sugar and reduces the risk of metabolic disorders. Regular physical activity enhances how cells respond to insulin….
Signs of Diabetes: Recognizing the Red Flags
Key Takeaways Increased Thirst and Urination: High blood sugar leads to dehydration, causing excessive thirst and frequent urination. Unexplained Weight Loss: Diabetes can cause the…
SIBO Bloating: Causes, Diet, & Management Tips
Key Takeaways SIBO disrupts gut bacteria balance, causing bloating, pain, and nutrient absorption issues. Symptoms include bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, and fatigue….
7 Remedies for Kidney Stones: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Takeaways Staying well-hydrated and adopting a balanced diet can help prevent kidney stones. Knowing the causes of kidney stones can inform effective prevention strategies….
Allergy-Friendly Pets
Key Highlights Hypoallergenic pets are great for people with pet allergies, as they produce fewer allergens like dander, saliva, and proteins that can trigger symptoms….
Metabolic Health: What It Means and How to Improve It
Key Takeaways Metabolic health reflects how well your body processes energy and maintains stable blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure. Key indicators of metabolic health…
Diabetes: Everything You Need to Know
Dialysis: Benefits & Challenges
Key Takeaways Dialysis removes waste and excess fluid from the blood when kidneys cannot function. Two main types: hemodialysis (machine-based) and peritoneal dialysis (abdomen-based). Dialysis…
7 Simple Tips for Lowering Blood Pressure Naturally
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is essential for overall well-being, as high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications. However, it is possible to…
High Homocysteine: How to Manage Levels
Key Takeaways: Elevated homocysteine can raise the risk of heart disease and other health problems. Animal-based foods high in B vitamins help reduce homocysteine levels….
Alcohol and Its Effects
Key Takeaways Alcohol is metabolized primarily in the liver, producing acetaldehyde, a toxic byproduct. Chronic alcohol consumption leads to liver damage, including fatty liver, hepatitis,…
Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Key Takeaways Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting memory, thinking, and behavior. Oxidative stress, including from excess iron, plays a significant role in…
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Causes & Treatment
Key Takeaways Ultra-processed foods and high carbohydrate intake worsen inflammation, harming kidney function. Iron overload leads to oxidative stress, which accelerates CKD progression. Copper is…
Supporting Mental Health with Gut Health
Key Takeaways Gut-Brain Connection: Gut health is directly linked to mental wellbeing through the gut-brain axis. Probiotics: Beneficial bacteria that help regulate mood and support…
Iron Overload: Symptoms & Prevention Tips
Key Takeaways: Iron overload happens when the body absorbs excessive iron, which can damage organs. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, and skin changes. Early…
Coping with Pet Allergies: Tips & Advice
Key Highlights Pet allergies often cause sneezing, coughing, itchy eyes, and skin rash. Pet allergens are in the saliva, urine, and dander of furry animals….
Travel Hygiene Tips: Stay Fresh on the Go
Key Highlights Key practices include frequent handwashing, showering, and oral care. Packing a portable hygiene kit can help you stay fresh on the go. Advanced…
Uric Acid: Effects & Management
Key Takeaways Uric acid plays a central role in metabolic health and oxidative stress regulation. Elevated uric acid levels are linked to gout, metabolic syndrome,…
Triglycerides: Levels & Range Explained
Key Highlights Triglycerides are the most common form of fat in the body play a role in energy storage High levels of triglycerides can increase…
Histamine: What You Should Know
Key Takeaways Histamine’s Role: Vital in immune responses, digestion, and as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Histamine Production: Produced in mast cells and…
Is Eating Sugar Really That Bad For Your Health?
Should You Really Be Concerned? In short, YES! Thank you, that’s all folks, and do have a good evening. Seriously though, extensive research has established…
Vegetable Oil: Health Risks You Might Not Know
Key Takeaways: Omega-6 fats from vegetable oils cause oxidative stress and inflammation. Reducing omega-6 intake and using stable fats can lower health risks. High triglycerides…
How to Lower Triglycerides Fast: Natural Solutions
Key Highlights Triglycerides, a type of fat found in the blood, are essential indicators of metabolic health. Elevated triglyceride levels increase the risk of heart…
Quit Sugar for 14 Days: What Happens to Your Body?
Key Takeaways: Immediate Health Benefits of Reducing Sugar: In just two weeks, enjoy enhanced energy levels, weight loss, a reduced risk of chronic diseases, and…
Inflammation: Causes & Effects
Key Takeaways Inflammation is the body’s response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to health problems. Iron overload from artificial sources and…
Remnant Cholesterol (RC): Its Origins & Impact
Key Takeaways Remnant cholesterol (RC) is the cholesterol content left in the blood after triglycerides are removed from VLDL and IDL particles. RC is a…
Metabolic Syndrome: Managing This Health Risk
Key Takeaways Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Symptoms include high blood pressure, high blood…
Atherosclerosis Prevention Strategies: Insights from Scientific Research
Key Takeaways Atherosclerosis is the hardening and narrowing of arteries caused by plaque buildup. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress contribute to the development of plaque….
Postbiotics: What They Are and Why They Are Important
Key Takeaways Postbiotics 101: They’re beneficial by-products from probiotics that consume prebiotics Boosts Immunity: Postbiotics sharpen your immune system, helping fight off pathogens and reducing…
Sunburn Prevention: Holistic and Natural Approaches
Key Takeaways A poor diet increases the risk of sunburn and skin damage. Short, regular…
Allergy-Friendly Pets
Key Highlights Hypoallergenic pets are great for people with pet allergies, as they produce fewer…
The Magnesium Factor by Dr. Mildred Seelig & Dr. Andrea Rosanoff
Key Takeaways Explores magnesium’s role in cardiovascular health. Discusses interaction between magnesium and other minerals….
Superoxide Dismutase: Your Body’s Antioxidant Defender
Key Takeaways SOD protects against oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals. Copper is necessary for…
Protein: You probably need more
Key Takeaways Protein is needed for building and repairing body tissues. It supports muscle growth,…
Insulin Resistance: What It Is & How to Manage It
Key Takeaways Insulin resistance leads to high blood sugar when cells stop responding to insulin….
What is the Best Nutrition for Pregnancy?
Key Takeaways Eating wisely during pregnancy impacts maternal and fetal health. Prioritize foods with a…
Creatine Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways Common myths about creatine, such as it causing kidney damage, weight gain, and…
Diabetes: Everything You Need to Know
Key Takeaways Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes involve insulin regulation issues, with Type 2…
9 Natural Ways to Repel Snails & Slugs in Your Garden
Key Highlights Coffee grounds, eggshells, and diatomaceous earth are effective natural repellents for snails and…
7 Key Hormones for Fat Burning
Key Takeaways: Hormones play a key role in regulating fat mobilization and utilization in the…