Key Takeaways
- Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) is a compound found naturally in various foods and offers several health benefits.
- TMG supports liver health by reducing fatty liver disease and aiding detoxification.
- It helps reduce homocysteine levels, promoting cardiovascular health.
- TMG enhances digestive health and improves nutrient absorption.
- It can boost muscle strength and athletic performance.
Introduction
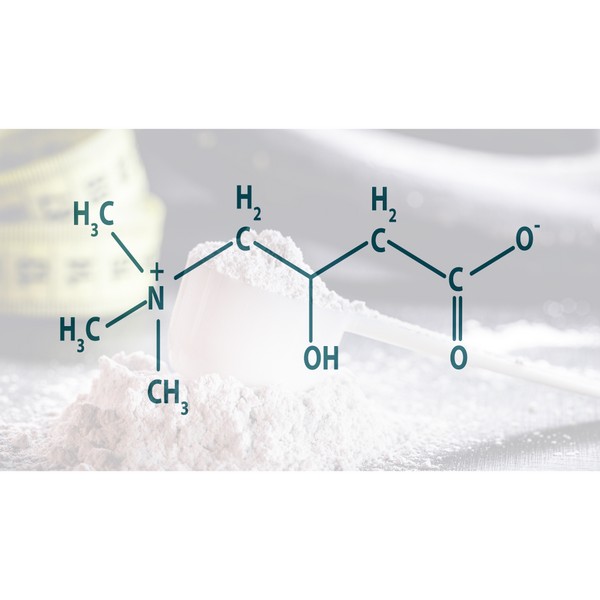
Betaine Anhydrous, also known as Trimethylglycine (TMG), is a naturally occurring compound found in various foods.
It’s gaining popularity in the health and wellness community due to its wide range of benefits.
What is Betaine Anhydrous (TMG)?
Betaine Anhydrous is a compound derived from the amino acid glycine. It is known for its role in supporting methylation processes in the body, which are crucial for various cellular functions.
Health Benefits of Betaine Anhydrous (TMG)
Liver Health
Betaine Anhydrous is beneficial for liver health. It helps reduce the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can prevent and manage fatty liver disease.
This is particularly important for individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition increasingly common due to poor dietary habits and sedentary lifestyles.
TMG supports liver detoxification processes, helping the liver efficiently eliminate toxins from the body.
Cardiovascular Health
TMG plays a significant role in cardiovascular health. One of its primary functions is to reduce homocysteine levels in the blood.
High levels of homocysteine are associated with an increased risk of heart disease. As it converts homocysteine into methionine, TMG helps maintain healthy homocysteine levels, thereby supporting heart health and potentially lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Digestive Health
Betaine Anhydrous also supports digestive health. It aids in the production of stomach acid, which is essential for proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
Adequate stomach acid levels help break down food more effectively, allowing for better absorption of nutrients and promoting overall gut health.
TMG’s role in maintaining a healthy digestive system can alleviate symptoms of indigestion and improve nutrient utilization.
Physical Performance and Muscle Strength

Athletes and fitness enthusiasts can benefit from TMG supplementation. Studies have shown that TMG can enhance muscle strength and improve physical performance.
It helps increase muscle protein synthesis, leading to greater muscle mass and strength gains.
Additionally, TMG has been found to improve endurance and reduce fatigue, making it a valuable supplement for those engaged in intense physical activities.
How Does Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) Work?
Betaine Anhydrous works primarily through its role in methylation processes. Methylation is a biochemical process that involves the transfer of methyl groups to various molecules, including DNA, proteins, and lipids.
This process is crucial for many cellular functions, including gene expression, protein function, and cell membrane integrity.
TMG donates a methyl group to homocysteine, converting it into methionine. This helps reduce homocysteine levels, supporting cardiovascular health.
Additionally, TMG’s role in methylation contributes to its liver-protective and muscle-enhancing effects.
TMG in Foods and Supplements

TMG is naturally present in various foods, with beets having one of the highest amount. Other foods high in Betaine Anhydrous include seafood and certain meats.
However, dietary sources may not always provide sufficient amounts for therapeutic benefits. This is where supplements come in.
TMG supplements are available in various forms, including powders, capsules, and tablets. They offer a convenient way to ensure you get an adequate amount of TMG to support your health goals.
Recommended Dosage and Usage
The recommended dosage of Betaine Anhydrous varies depending on the intended use. For general health benefits, a typical dosage ranges from 500 mg to 2,000 mg per day.
For liver health and cardiovascular support, doses of 1,000 mg to 3,000 mg per day are common. Athletes looking to enhance performance may take up to 2,500 mg to 5,000 mg per day.
It’s best to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it to assess tolerance. Betaine Anhydrous can be taken with or without food.
However, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Nutricost
Trimethyglycine
- TMG: Also known as glycine betaine; contains three methyl groups.
- Whole-Body Wellness: TMG reduces homocysteine levels, enhancing systemic health.
- The Healthy Choice: Gluten-free, non-GMO.
Combining TMG with Other Supplements
Betaine Anhydrous can be combined with bee pollen and nutritional yeast to support methylation processes more effectively.
Synthetic B vitamins are not recommended as they do not function the correct way food-based sources do inside the body.
Conclusion
Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) is a versatile compound with numerous health benefits. From supporting liver health and cardiovascular function to enhancing digestive health and muscle strength, TMG offers a range of advantages. By incorporating TMG into your health regimen, you can take advantage of its benefits and improve your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between Betaine Anhydrous and Betaine HCl?
Betaine Anhydrous is a form of betaine without water molecules, while Betaine HCl is a form of betaine combined with hydrochloric acid. Betaine HCl is primarily used to increase stomach acid levels, while Betaine Anhydrous is used for its broader health benefits.
Can TMG help with weight loss?
While TMG is not specifically marketed for weight loss, its role in supporting liver health and improving muscle strength can indirectly contribute to weight management. A healthy liver and increased muscle mass can enhance metabolism and aid in maintaining a healthy weight.
Is TMG safe for long-term use?
TMG is generally considered safe for long-term use when taken within recommended dosages. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially for long-term use.
How quickly can I expect to see results from TMG supplementation?
The time it takes to see results from TMG supplementation can vary depending on individual factors and health goals. Some people may notice improvements in energy levels and digestion within a few days, while others may take several weeks to experience significant benefits.
Research
Ashtary-Larky, D., Bagheri, R., Ghanavati, M., Asbaghi, O., Tinsley, G. M., Mombaini, D., … Wong, A. (2021). Effects of betaine supplementation on cardiovascular markers: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 62(23), 6516–6533.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1902938
Craig, S. A. (2004). Betaine in human nutrition. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 80(3), 539-549. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/80.3.539
Grizales, A. M., Patti, M., Lin, A. P., Beckman, J. A., Sahni, V. A., Cloutier, E., Fowler, K. M., Dreyfuss, J. M., Pan, H., Kozuka, C., Lee, A., Basu, R., Pober, D. M., Gerszten, R. E., & Goldfine, A. B. (2018). Metabolic Effects of Betaine: A Randomized Clinical Trial of Betaine Supplementation in Prediabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 103(8), 3038-3049.
Hoffman, J.R., Ratamess, N.A., Kang, J., Rashti, S.L. and Faigenbaum, A.D., 2009. Effect of betaine supplementation on power performance and fatigue. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, [online] 6(1).
https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-6-7
Kadokawa, R., Fujie, T., Sharma, G., Ishibashi, K., Ninomiya, K., Takahashi, K., Hirata, E., & Kuroda, K. (2021). High loading of trimethylglycine promotes aqueous solubility of poorly water-soluble cisplatin. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89144-0
Lever, M., & Slow, S. (2010). The clinical significance of betaine, an osmolyte with a key role in methyl group metabolism. Clinical Biochemistry, 43(9), 732-744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2010.03.009
McRae, M. P. (2013). Betaine supplementation decreases plasma homocysteine in healthy adult participants: A meta-analysis. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine, 12(1), 20-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2012.11.001
Schwab, U., Törrönen, A., Meririnne, E., Saarinen, M., Alfthan, G., Aro, A., & Uusitupa, M. (2006). Orally Administered Betaine Has an Acute and Dose-Dependent Effect on Serum Betaine and Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations in Healthy Humans. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 34-38. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.1.34
Schwab, U., Törrönen, A., Toppinen, L., Alfthan, G., Saarinen, M., Aro, A., & Uusitupa, M. (2002). Betaine supplementation decreases plasma homocysteine concentrations but does not affect body weight, body composition, or resting energy expenditure in human subjects,,. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 76(5), 961-967. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/76.5.961
Steenge, G. R., Verhoef, P., & Katan, M. B. (2003). Betaine Supplementation Lowers Plasma Homocysteine in Healthy Men and Women. The Journal of Nutrition, 133(5), 1291-1295. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.5.1291
Creatine Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways Common myths about creatine, such as it causing kidney damage, weight gain, and being a steroid, are widespread but unsupported by scientific evidence….
Taurine: The Mighty Amino Acid for Optimal Health
Key Takeaways Taurine supports heart health, regulates blood pressure, and reduces oxidative stress. Essential for muscle function, brain health, and cognitive function. Aids in insulin…
TUDCA Benefits for Health
Key Takeaways TUDCA promotes liver health, aiding cell protection and repair. Enhances digestion by improving bile flow and supporting gut health. May protect brain health…
Spirulina: Health Benefits and Uses
Key Takeaways Spirulina boosts immune function with its high nutrient content and antioxidant properties. Rich in proteins and essential vitamins, enhances overall nutrition. Helps reduce…
Berberine Has 11 More Incredible Benefits Than You Thought
Berberine is a compound found in several plants that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda. It has recently gained popularity…
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA): Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways CLA is a type of fatty acid found primarily in animal products like beef and dairy. Known for potential benefits such as weight…
Vitamin E Complex
Key Takeaways Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. The vitamin E complex includes…
Postbiotics: What They Are and Why They Are Important
Key Takeaways Postbiotics 101: They’re beneficial by-products from probiotics that consume prebiotics Boosts Immunity: Postbiotics sharpen your immune system, helping fight off pathogens and reducing…
L-Carnitine: Benefits, Dosage, and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Carnitine supports fat metabolism and energy production. Benefits include enhanced exercise performance and improved heart health. Proper dosing minimizes potential side effects. Understanding…
Medium Chain Triglycerides (MCTs): Uncovering 5 Health Benefits
This potent, natural source of energy has gained considerable attention in recent years for its impressive array of benefits. MCT oil is a versatile addition…
L-Glutamine and Gut Health: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Glutamine is essential for gut health. Benefits include improved digestion and reduced inflammation. Potential side effects are rare but can occur in high…