Key Highlights
- Triglycerides, a type of fat found in the blood, are essential indicators of metabolic health.
- Elevated triglyceride levels increase the risk of heart disease and related conditions.
- Focusing on animal products may help reduce triglyceride levels for some individuals.
- Lowering triglycerides naturally involves a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and weight control.
- Supplements like cod liver oil can support healthy triglyceride levels.
Natural Ways to Lower Triglycerides

In addition to not smoking, eating healthy food is a major lever you could pull to bring down high triglyceride levels.
Foods to Include for Lowering Triglycerides
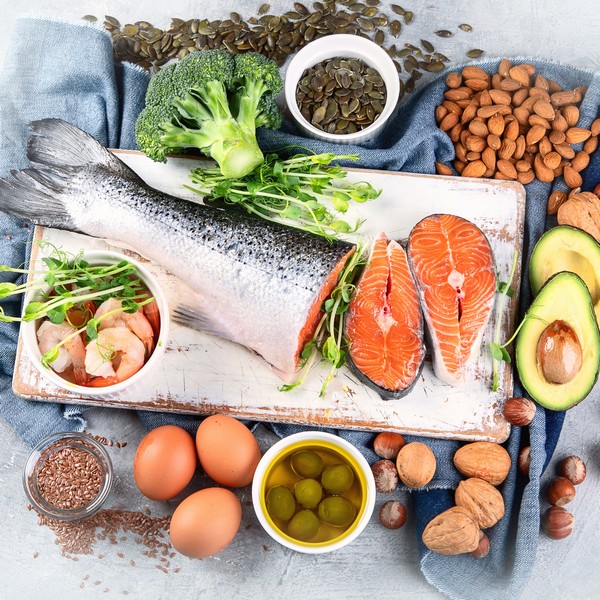
Always choose the more nutrient-dense, highly bioavailable foods that are high in healthy fats and animal proteins, such as:
Foods to Avoid to Keep Triglycerides in Check

It’s up to you to decide. The more you remove the following the better your triglyceride levels will be.
- Carbohydrates
- Ultra-processed food
- Alcohol
The Impact of Lifestyle on Triglyceride Levels
Regular exercise and stress management help to reduce triglyceride levels. Physical activity helps the body use fats more efficiently, lowering triglycerides.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also important, as excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can elevate triglyceride levels.
Stress reduction techniques like meditation and deep breathing can improve lipid profiles and overall heart health.
Exercise Strategies to Reduce Triglycerides

Engage in regular physical activity to manage triglyceride levels. Aim for:
- 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week
- Activities such as walking, biking, swimming, or dancing
- Muscle-strengthening exercises like weight lifting or resistance band workouts
Weight Management and Its Effect on Lipids
Maintaining a healthy weight significantly impacts triglyceride levels and heart health. Weight loss, even in small amounts, can lower triglycerides and improve lipid profiles.
Easily achieve this through a low carbohydrate diet and regular exercise.
Stress Reduction Techniques for Better Lipid Profiles
Stress can increase triglyceride levels due to elevated stress hormones. Some techniques can reduce stress and lower triglyceride levels, promoting better heart health.
- meditation
- deep breathing
- yoga
- engaging in enjoyable hobbies
Supplements for Triglyceride Management

Supplements can complement lifestyle changes in managing triglyceride levels. Notable supplements include:
Fenugreek
Fenugreek, a herb commonly used in Indian cuisine, may help lower triglyceride levels due to its high dietary fiber content, which stabilizes blood sugar and boosts metabolism.
Turmeric
Turmeric, containing curcumin, has anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce triglyceride levels and improve heart health.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid
Alpha-lipoic acid acts as a potent antioxidant, reducing oxidative stress and improving insulin sensitivity, which can help lower triglyceride levels. Foods rich in lipoic acid red meat and organ meats.
Lavender
Lavender may indirectly lower triglyceride levels by reducing stress. Use lavender in essential oils, teas, or as a culinary herb to promote relaxation.
Lemongrass
Lemongrass can improve heart health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels, thereby helping to manage triglyceride levels.
Holy Basil
Holy Basil (Tulsi) can lower blood sugar levels and reduce stress, both of which contribute to healthier triglyceride levels.

Conclusion
Managing triglyceride levels is essential for heart health and preventing metabolic disorders. Adopting a diet focused on nutrient-dense, bioavailable animal proteins and fats, such as red meat, full-fat dairy, and fatty fish, can significantly lower triglycerides. This dietary approach, combined with lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, stress management, and weight control, enhances your ability to maintain healthy triglyceride levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Triglycerides Be Quickly Lowered Through Diet Alone?
Diet plays a significant role in lowering triglycerides. Focus on a high-fiber, low-sugar diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Regular exercise complements dietary changes for optimal results.
How Often Should I Monitor My Triglyceride Levels?
Annual monitoring of triglyceride levels is recommended, especially if you have a history of high triglycerides or cardiovascular disease. Regular checks help track progress and adjust lifestyle changes as needed.
Are There Any Quick Fixes to Lower Triglycerides?
There are no instant solutions for lowering triglycerides. Sustainable changes in diet and lifestyle, such as reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing physical activity, are effective over time. Consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
What Is the Best Exercise for Lowering Triglycerides?
Cardio exercises like brisk walking, running, biking, or swimming are effective in reducing triglyceride levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly, complemented by muscle-strengthening activities.
How Long Does It Take to See Results from Lifestyle Changes?
Results from lifestyle changes can vary. Many individuals see improvements in triglyceride levels within a few weeks to months. Consistent healthy habits and regular monitoring are key to long-term success. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and adjustments.
Research
Aviram, M., Brox, J. and Nordoy, A., 1986. Acute Effects of Dietary Cod Liver Oil and Cream on Plasma Lipoproteins. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, [online] 30(2), pp.143–148.
https://doi.org/10.1159/000177187.
Banta, J.E., Lee, J.W., Hodgkin, G., Yi, Z., Fanica, A. and Sabate, J., 2018. The Global Influence of the Seventh-Day Adventist Church on Diet. Religions, [online] 9(9), p.251.
https://doi.org/10.3390/rel9090251.
Burchard HU, Tischendorf FW. Die Auswirkungen der Einnahme von Lebertran auf den Blutfettspiegel, das Lipoproteinprofil und die Blutungszeit [The effects of the intake of cod liver oil on the blood lipid level, the lipoprotein profile and bleeding time]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1989 Mar;28(1):84-91. German. doi: 10.1007/BF02025568. PMID: 2718528.
Dibaba DT. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum lipid profiles: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. 2019 Dec 1;77(12):890-902. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuz037. PMID: 31407792.
Egeland, G. M., Meyer, H. E., Selmer, R., Tverdal, A., & Vollset, S. E. (2001). Cod Liver Oil Consumption, Smoking, and Coronary Heart Disease Mortality: Three Counties, Norway. International Journal of Circumpolar Health, 60(2), 143–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/25761900.2022.12220584
Fatima, F., Memon, A., Zafar, S., Amar, Z., Talpur, A. S., Hashim, S., Maqsood, H., Hafizyar, F., & Kumar, B. (2021). Role of Cod Liver Oil in Reducing Elevated Lipid Parameters. Cureus, 13(6).
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.15556
Goel S, Sharma A, Garg A. Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Cardiovascular Health. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018 Mar 8;20(4):19. doi: 10.1007/s11886-018-0962-2. PMID: 29520541.
Heden, T., Liu, Y., Sims, L., Whaley-Connell, A. T., Chockalingam, A., Dellsperger, K. C., & Kanaley, J. A. (2013). Meal frequency differentially alters postprandial triacylglycerol and insulin concentrations in obese women. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 21(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.20247
HODGES, R. E., & KREHL, W. (1965). The Role of Carbohydrates in Lipid Metabolism. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 17(5), 334-346. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/17.5.334
Hudgins, L.C., 2000. Effect of High-Carbohydrate Feeding on Triglyceride and Saturated Fatty Acid Synthesis. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, [online] 225(3), pp.178–183. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1373.2000.22521.x.
Iqbal, M. P. Trans fatty acids – A risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences, 30(1), 194-197. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.301.4525
Irfan, N., Bilal, A., Ullah, M. A., Tufail, T., Ullah, I., & Yousaf, A. A. (2022). EVALUATING THE EFFECT OF BASIL SEEDS (OCIMUM BASILICUM) ON HYPERLIPIDEMIA. Pakistan Journal of Biotechnology, 19(02), 136–147. https://doi.org/10.34016/pjbt.2022.19.2.106
McCarty, M. F. (2004). An elevation of triglycerides reflecting decreased triglyceride clearance may not be pathogenic – relevance to high-carbohydrate diets. Medical Hypotheses, 63(6), 1065-1073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2002.11.002
Min, H. S., Kang, J. Y., Sung, J., & Kim, M. K. (2016). Blood Triglycerides Levels and Dietary Carbohydrate Indices in Healthy Koreans. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, 49(3), 153-164. https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.16.014
Natto, Z. S., Yaghmoor, W., Alshaeri, H. K., & Van Dyke, T. E. (2019). Omega-3 Fatty Acids Effects on Inflammatory Biomarkers and Lipid Profiles among Diabetic and Cardiovascular Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54535-x
Qin, S., Huang, L., Gong, J., Shen, S., Huang, J., Ren, H., & Hu, H. (2017). Efficacy and safety of turmeric and curcumin in lowering blood lipid levels in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition Journal, 16.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-017-0293-y
Rafraf M, Malekiyan M, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Aliasgarzadeh A. Effect of Fenugreek Seeds on Serum Metabolic Factors and Adiponectin Levels in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2014;84(3-4):196-205. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000206. PMID: 26098483.
Raatz SK, Johnson LK, Rosenberger TA, Picklo MJ. Twice weekly intake of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) positively influences lipoprotein concentration and particle size in overweight men and women. Nutr Res. 2016 Sep;36(9):899-906. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 27. PMID: 27632909.
Rosales, C., Gillard, B. K., & Pownall, H. J. (2020). The Alcohol–High-Density Lipoprotein Athero-Protective Axis. Biomolecules, 10(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10070987
Smith, U. (1994). Carbohydrates, fat, and insulin action. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 59(3), 686S-689S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/59.3.686S
Taylor AE, Lu F, Carslake D, Hu Z, Qian Y, Liu S, Chen J, Shen H, Smith GD. Exploring causal associations of alcohol with cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors in a Chinese population using Mendelian randomization analysis. Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 14;5:14005. doi: 10.1038/srep14005. PMID: 26364564; PMCID: PMC4568464.
Truswell, A. (1994). Food carbohydrates and plasma lipids””an update. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 59(3), 710S-718S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/59.3.710S
Ullrich, I.H., Peters, P.J. and Albrink, M.J., 1985. Effect of low-carbohydrate diets high in either fat or protein on thyroid function, plasma insulin, glucose, and triglycerides in healthy young adults. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, [online] 4(4), pp.451–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.1985.10720087.
Wolever, T., Gibbs, A., Chiasson, J., Connelly, P., Josse, R., Leiter, L., Maheux, P., Rabasa-Lhoret, R., Rodger, N., & Ryan, E. (2013). Altering source or amount of dietary carbohydrate has acute and chronic effects on postprandial glucose and triglycerides in type 2 diabetes: Canadian trial of Carbohydrates in Diabetes (CCD). Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, 23(3), 227-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2011.12.011
Yang, J., Wu, L., & Chiu, H. (2018). High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise Increases Fat Oxidation Rate and Reduces Postprandial Triglyceride Concentrations. Nutrients, 10(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040492
Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Key Takeaways Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting memory, thinking, and behavior. Oxidative stress, including from excess iron, plays a significant role in…
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Causes & Treatment
Key Takeaways Ultra-processed foods and high carbohydrate intake worsen inflammation, harming kidney function. Iron overload leads to oxidative stress, which accelerates CKD progression. Copper is…
SIBO Bloating: Causes, Diet, & Management Tips
Key Takeaways SIBO disrupts gut bacteria balance, causing bloating, pain, and nutrient absorption issues. Symptoms include bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, and fatigue….
Boost Insulin Sensitivity Naturally
Key Takeaways Improving insulin sensitivity helps control blood sugar and reduces the risk of metabolic disorders. Regular physical activity enhances how cells respond to insulin….
How to Lower Triglycerides Fast: Natural Solutions
Key Highlights Triglycerides, a type of fat found in the blood, are essential indicators of metabolic health. Elevated triglyceride levels increase the risk of heart…
Insulin Resistance: What It Is & How to Manage It
Key Takeaways Insulin resistance leads to high blood sugar when cells stop responding to insulin. Often connected to obesity, poor diet, and physical inactivity. Symptoms…
7 Simple Tips for Lowering Blood Pressure Naturally
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is essential for overall well-being, as high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications. However, it is possible to…
Vegetable Oil: Health Risks You Might Not Know
Key Takeaways: Omega-6 fats from vegetable oils cause oxidative stress and inflammation. Reducing omega-6 intake and using stable fats can lower health risks. High triglycerides…
Alcohol and Its Effects
Key Takeaways Alcohol is metabolized primarily in the liver, producing acetaldehyde, a toxic byproduct. Chronic alcohol consumption leads to liver damage, including fatty liver, hepatitis,…
Histamine: What You Should Know
Key Takeaways Histamine’s Role: Vital in immune responses, digestion, and as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Histamine Production: Produced in mast cells and…
Supporting Mental Health with Gut Health
Key Takeaways Gut-Brain Connection: Gut health is directly linked to mental wellbeing through the gut-brain axis. Probiotics: Beneficial bacteria that help regulate mood and support…
Diabetes: Everything You Need to Know
Key Takeaways Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes involve insulin regulation issues, with Type 2 being the most common due to insulin resistance. Copper, retinol,…
Coping with Pet Allergies: Tips & Advice
Key Highlights Pet allergies often cause sneezing, coughing, itchy eyes, and skin rash. Pet allergens are in the saliva, urine, and dander of furry animals….
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Key Takeaways NAFLD involves fat buildup in the liver not caused by alcohol. Commonly associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can lead…
Uric Acid: Effects & Management
Iron Overload: Symptoms & Prevention Tips
Key Takeaways: Iron overload happens when the body absorbs excessive iron, which can damage organs. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, and skin changes. Early…
Is Eating Sugar Really That Bad For Your Health?
Should You Really Be Concerned? In short, YES! Thank you, that’s all folks, and do have a good evening. Seriously though, extensive research has established…
Inflammation: Causes & Effects
Key Takeaways Inflammation is the body’s response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to health problems. Iron overload from artificial sources and…
Metabolic Health: What It Means and How to Improve It
Key Takeaways Metabolic health reflects how well your body processes energy and maintains stable blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure. Key indicators of metabolic health…
Signs of Diabetes: Recognizing the Red Flags
Key Takeaways Increased Thirst and Urination: High blood sugar leads to dehydration, causing excessive thirst and frequent urination. Unexplained Weight Loss: Diabetes can cause the…
Remnant Cholesterol (RC): Its Origins & Impact
Key Takeaways Remnant cholesterol (RC) is the cholesterol content left in the blood after triglycerides are removed from VLDL and IDL particles. RC is a…
High Homocysteine: How to Manage Levels
Key Takeaways: Elevated homocysteine can raise the risk of heart disease and other health problems. Animal-based foods high in B vitamins help reduce homocysteine levels….
Allergy-Friendly Pets
Key Highlights Hypoallergenic pets are great for people with pet allergies, as they produce fewer allergens like dander, saliva, and proteins that can trigger symptoms….
Proteolytic Enzymes and Heart Health: What the Research Shows
Your heart works tirelessly to pump blood throughout your body, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to your cells. However, factors like poor diet, stress, and…
Parkinson’s Disease : Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Key Takeaways Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement and coordination. Oxidative stress and excess iron are significant factors in the progression…
Dialysis: Benefits & Challenges
Key Takeaways Dialysis removes waste and excess fluid from the blood when kidneys cannot function. Two main types: hemodialysis (machine-based) and peritoneal dialysis (abdomen-based). Dialysis…
7 Remedies for Kidney Stones: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Takeaways Staying well-hydrated and adopting a balanced diet can help prevent kidney stones. Knowing the causes of kidney stones can inform effective prevention strategies….
Quit Sugar for 14 Days: What Happens to Your Body?
Key Takeaways: Immediate Health Benefits of Reducing Sugar: In just two weeks, enjoy enhanced energy levels, weight loss, a reduced risk of chronic diseases, and…
Metabolic Syndrome: Managing This Health Risk
Key Takeaways Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Symptoms include high blood pressure, high blood…
Travel Hygiene Tips: Stay Fresh on the Go
Key Highlights Key practices include frequent handwashing, showering, and oral care. Packing a portable hygiene kit can help you stay fresh on the go. Advanced…
Atherosclerosis Prevention Strategies: Insights from Scientific Research
Key Takeaways Atherosclerosis is the hardening and narrowing of arteries caused by plaque buildup. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress contribute to the development of plaque….
Postbiotics: What They Are and Why They Are Important
Key Takeaways Postbiotics 101: They’re beneficial by-products from probiotics that consume prebiotics Boosts Immunity: Postbiotics sharpen your immune system, helping fight off pathogens and reducing…
Triglycerides: Levels & Range Explained
Key Highlights Triglycerides are the most common form of fat in the body play a role in energy storage High levels of triglycerides can increase…
L-Glutamine and Gut Health: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Glutamine is essential for gut health. Benefits include improved digestion and reduced inflammation. Potential side effects are rare but can occur in high…