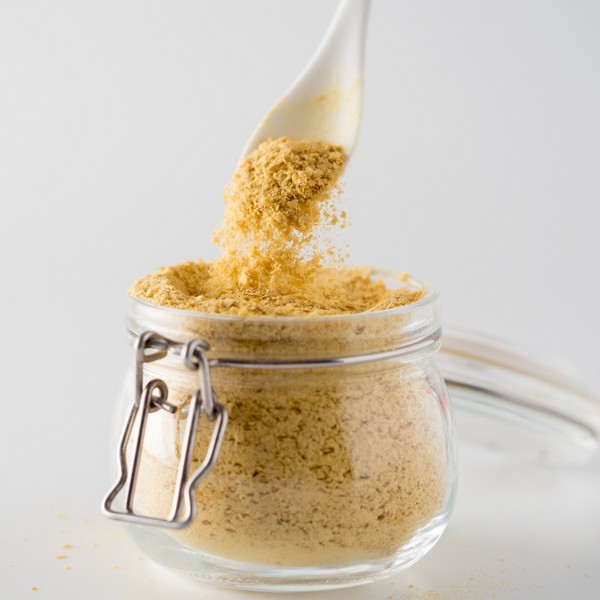
Key Takeaways
– Stabilized rice bran is a nutrient-rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
– The stabilization process prevents rancidity, making it a long-lasting and healthy food ingredient.
– It supports digestive health, cholesterol management, and heart health.
– Stabilized rice bran contains essential nutrients like B vitamins, magnesium, and healthy fats.
– It is versatile and can be added to various dishes, such as smoothies and baked goods.
What is Stabilized Rice Bran?

Stabilized rice bran is the outer layer of the rice grain, rich in nutrients but prone to spoilage. To prevent it from turning rancid, the bran undergoes a stabilization process that extends its shelf life while preserving its nutritional value.
Unlike unstabilized rice bran, which spoils quickly, stabilized rice bran can be stored and used for a longer time without losing its benefits.
Difference Between Stabilized and Unstabilized Rice Bran
Unstabilized rice bran spoils quickly due to the presence of natural oils that turn rancid when exposed to air.
Stabilization heats the bran, deactivating the enzymes that cause spoilage, making the product safe for long-term use while maintaining its rich nutrient profile.
Nutritional Composition of Stabilized Rice Bran

Vitamins (B Vitamins, Vitamin E)
Stabilized rice bran is a good source of B vitamins, which are essential for energy production and overall cellular function.
It also contains vitamin E, an antioxidant that supports skin health and protects cells from oxidative damage.
Minerals (Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium)
It provides key minerals like magnesium, which supports muscle and nerve function, phosphorus for bone health, and potassium, which helps maintain proper fluid balance in the body.
Antioxidants (Tocopherols, Tocotrienols)
Stabilized rice bran is rich in antioxidants, including tocopherols and tocotrienols, which protect the body from free radical damage and may support heart health by reducing oxidative stress.
Healthy Fats and Fiber
The bran is high in healthy fats, particularly unsaturated fats, which are good for heart health. It is also a great source of dietary fiber, promoting digestion and helping regulate blood sugar levels.
Health Benefits of Stabilized Rice Bran

The best use case for stabilized rice bran is for its ability to bind to excess iron. However, as a bonus, there are other beneficial effects.
- Rich in Nutrients: Contains high-quality protein, gamma-oryzanol, vitamins, and minerals beneficial for overall health.
- Antioxidant Properties: Neutralizes free radicals and reduces oxidative stress, protecting against cell damage.
- Supports Glycemic Control: Helps lower fasting blood sugar, improves insulin secretion, and reduces HbA1c in diabetics.
- Lipid-Lowering Effect: Reduces triglycerides while potentially increasing HDL cholesterol.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Reduces inflammation markers and increases anti-inflammatory cytokines.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Peptides in rice bran improve endothelial function and lower systolic blood pressure.
- Supports Gut Health: Promotes bowel function, improves microbiota balance, and acts as a prebiotic.
- Weight Management: Helps regulate lipid metabolism and reduce abdominal fat in certain cases.
- Liver and Kidney Protection: Mitigates the effects of oxidative stress and inflammation on liver and kidney functions.
- Safe for Consumption: Recognized as safe with no mutagenic or teratogenic effects at approved levels.
Uses of Stabilized Rice Bran
As a Dietary Supplement
Stabilized rice bran is often used as a supplement due to its rich nutrient profile. It can be taken as a powder or capsule to boost daily intake of vitamins & minerals
Adding to Smoothies, Baked Goods, and Cereals
This ingredient is highly versatile and can be added to smoothies, baked goods, and cereals for an extra nutritional boost. Its mild flavor blends well with a variety of foods.
As an Ingredient in Health Products
Many health and wellness products incorporate stabilized rice bran due to its nutritional benefits. It can be found in protein powders, health bars, and functional foods designed to support overall wellness.
Processing and Stabilization

How Rice Bran is Stabilized
Stabilization involves heating the rice bran to deactivate the lipase enzyme, which causes spoilage.
This process preserves the nutritional content and extends its shelf life, making it a more reliable and long-lasting ingredient.
Preventing Rancidity and Preserving Nutrients
Stabilizing rice bran not only prevents rancidity but also ensures that its nutrients remain intact. The heating process used in stabilization is carefully controlled to maintain the quality of the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in the bran.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Digestive Sensitivity in Some Individuals
While most people tolerate stabilized rice bran well, its high fiber content may cause digestive discomfort in some individuals, particularly if they are not used to consuming large amounts of fiber. It’s recommended to introduce it gradually into the diet.
Nutrient Absorption Considerations
The fiber in rice bran may affect the absorption of certain nutrients if consumed in large quantities. It’s important to maintain a balanced diet to ensure adequate nutrient intake when adding high-fiber foods like rice bran.
FAQs
What makes stabilized rice bran different from regular rice bran?
Stabilized rice bran has been heated to deactivate enzymes that cause spoilage, making it longer-lasting and nutritionally stable compared to regular rice bran.
How much stabilized rice bran should I consume daily?
Most people can safely consume about 1-2 tablespoons of stabilized rice bran per day, though it’s best to start with smaller amounts to see how your body responds.
Can stabilized rice bran help with weight management?
Yes, the fiber content in stabilized rice bran promotes fullness, helping to manage appetite and support weight control when included in a balanced diet.
Is stabilized rice bran gluten-free?
Yes, stabilized rice bran is naturally gluten-free, making it a safe option for individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
How do I store stabilized rice bran to keep it fresh?
Store stabilized rice bran in a cool, dry place in an airtight container to maintain its freshness. Keeping it in the refrigerator can further extend its shelf life.
Research
Anon. 2018. EFFECT OF SOME STABILIZATION METHODS ON NUTRITIONAL COMPOSITION OF RICE BRAN. Zagazig Journal of Agricultural Research, [online] 45(3), pp.985–994. https://doi.org/10.21608/zjar.2018.49147.
Bhosale S, Vijayalakshmi D. Processing and Nutritional Composition of Rice Bran. Curr Res Nutr Food Sci 2015;3(1). doi : http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CRNFSJ.3.1.08
Brown DG, Borresen EC, Brown RJ, Ryan EP. Heat-stabilised rice bran consumption by colorectal cancer survivors modulates stool metabolite profiles and metabolic networks: a randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Nutrition. 2017;117(9):1244-1256. doi:10.1017/S0007114517001106
Demirci, T., Aktaş, K., Sözeri, D., Öztürk, H. İ., & Akın, N. (2017). Rice bran improve probiotic viability in yoghurt and provide added antioxidative benefits. Journal of Functional Foods, 36, 396-403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.07.019
Ertürk, B., & Meral, R. (2019). The impact of stabilization on functional, molecular and thermal properties of rice bran. Journal of Cereal Science, 88, 71-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2019.05.011
Faria, S.A.D.S.C., Bassinello, P.Z. and Penteado, M.D.V.C., 2012. Nutritional composition of rice bran submitted to different stabilization procedures. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 48, pp.651-657.
Foong, L.-C., Imam, M.U. and Ismail, M., 2015. Iron-Binding Capacity of Defatted Rice Bran Hydrolysate and Bioavailability of Iron in Caco-2 Cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, [online] 63(41), pp.9029–9036. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03420.
Gong, X., Sui, L., Morton, J., Brennan, M. A., & Brennan, C. S. (2021). Investigation of nutritional and functional effects of rice bran protein hydrolysates by using Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 110, 798-811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.089
Gul, K., Yousuf, B., Singh, A., Singh, P., & Wani, A. A. (2015). Rice bran: Nutritional values and its emerging potential for development of functional food—A review. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre, 6(1), 24-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2015.06.002
Irakli, M., Kleisiaris, F., Mygdalia, A., & Katsantonis, D. (2018). Stabilization of rice bran and its effect on bioactive compounds content, antioxidant activity and storage stability during infrared radiation heating. Journal of Cereal Science, 80, 135-142.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2018.02.005
Jeon, S.-J., Lee, J.-H. and Song, K.-B., 2010. Preparation for Calcium and Iron-binding Peptides from Rice Bran Protein Hydrolysates. Journal of Applied Biological Chemistry, [online] 53(3), pp.174–178. https://doi.org/10.3839/jabc.2010.031.
John N. Kinyuru, Erica C. Borresen, Elizabeth P. Ryan (2015) Nutritional and Safety Evaluation of Heat-Stabilized Rice Bran for Supplementary Feeding of Malnourished Children in Kenya. Int J Food SciNutr Diet. 04(6), 226-232. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.19070/2326-3350-1500041
Meng, F., Wei, Y., & Yang, X. (2005). Iron content and bioavailability in rice. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 18(4), 333-338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2005.02.008
Nagendra Prasad MN, N.P., KR, S. and Khatokar M, S., 2011. Health Benefits of Rice Bran - A Review. Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences, [online] 01(03).
https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9600.1000108.
Ooi, S. L., Micalos, P. S., & Pak, S. C. (2023). Modified rice bran arabinoxylan as a nutraceutical in health and disease—A scoping review with bibliometric analysis. PLOS ONE, 18(8), e0290314. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0290314
Ooi, S. L., Micalos, P. S., Kim, J., & Pak, S. C. (2024). Rice bran arabinoxylan compound as a natural product for cancer treatment – an evidence-based assessment of the effects and mechanisms. Pharmaceutical Biology, 62(1), 367–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2024.2349042
Park, H.-Y., Lee, K.-W. and Choi, H.-D., 2017. Rice bran constituents: immunomodulatory and therapeutic activities. Food & Function, [online] 8(3), pp.935–943. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo01763k.
Prakash, J., & Ramaswamy, H. S. (1996). Rice bran proteins: Properties and food uses. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 36(6), 537–552. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408399609527738
Rafe, A., Sadeghian, A., & Hoseini-Yazdi, S. Z. (2017). Physicochemical, functional, and nutritional characteristics of stabilized rice bran form tarom cultivar. Food Science & Nutrition, 5(3), 407-414. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.407
Raghav, P.K., Agarwal, N. and Sharma, A., 2016. Emerging health benefits of rice bran—A review. Int J Multidiscip Res Mod Educ, 2, pp.367-82.
Saji, N., Schwarz, L. J., Santhakumar, A. B., & Blanchard, C. L. (2020). Stabilization treatment of rice bran alters phenolic content and antioxidant activity. Cereal Chemistry, 97(2), 281-292. https://doi.org/10.1002/cche.10243
Sapwarobol, S., Saphyakhajorn, W., & Astina, J. (2021). Biological Functions and Activities of Rice Bran as a Functional Ingredient: A Review. Nutrition and Metabolic Insights.
https://doi.org/10.1177/11786388211058559
Scarano, A., Laddomada, B., Blando, F., Santis, S. D., Verna, G., Chieppa, M., & Santino, A. (2023). The Chelating Ability of Plant Polyphenols Can Affect Iron Homeostasis and Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants, 12(3), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030630
Sharif, M.K., Butt, M.S., Anjum, F.M. and Khan, S.H., 2013. Rice Bran: A Novel Functional Ingredient. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, [online] 54(6), pp.807–816. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2011.608586.
Sivasinprasasn, S., Tocharus, J., Mahatheeranont, S., Nakrat, S., & Tocharus, C. Anthocyanin-Rich Fraction of Black Rice Bran Extract Protects against Amyloid β-Induced Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Neuronal Apoptosis in SK-N-SH Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 17(8), 1039.
https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/17/8/1039
Tan, B. L., Norhaizan, M. E., & Chan, L. C. (2023). Rice Bran: From Waste to Nutritious Food Ingredients. Nutrients, 15(11), 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112503
Wang, N., Cui, X., Duan, Y., Yang, S., Wang, P., Saleh, A.S.M. and Xiao, Z., 2021. Potential health benefits and food applications of rice bran protein: research advances and challenges. Food Reviews International, [online] 39(6), pp.3578–3601. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2021.2013253.
Yılmaz Tuncel, N. Stabilization of Rice Bran: A Review. Foods, 12(9), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091924
Zinc Supplements: Risks and Dangers
Key Takeaways Zinc supports immunity, wound healing, and cell growth. High zinc supplement doses can cause health problems. Always consult a healthcare provider before taking…
Liver: 5 Surprising Benefits Backed by Science
Hold on! Don’t run away! You need to read this. Liver is a highly nutritious organ meat that is often overlooked in modern diets. Packed…
L-Carnitine: Benefits, Dosage, and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Carnitine supports fat metabolism and energy production. Benefits include enhanced exercise performance and improved heart health. Proper dosing minimizes potential side effects. Understanding…
Vitamin E Complex
Key Takeaways Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. The vitamin E complex includes…
Allulose: The Best Sugar Alternative
Key Takeaways Allulose is a low-calorie sweetener found naturally in some fruits. It does not raise blood sugar levels, making it suitable for diabetics. Allulose…
Postbiotics: What They Are and Why They Are Important
Key Takeaways Postbiotics 101: They’re beneficial by-products from probiotics that consume prebiotics Boosts Immunity: Postbiotics sharpen your immune system, helping fight off pathogens and reducing…
Is Eating Sugar Really That Bad For Your Health?
Should You Really Be Concerned? In short, YES! Thank you, that’s all folks, and do have a good evening. Seriously though, extensive research has established…
TUDCA Benefits for Health
Key Takeaways TUDCA promotes liver health, aiding cell protection and repair. Enhances digestion by improving bile flow and supporting gut health. May protect brain health…
CoQ10: What Is It and Why Is It Important?
Key Takeaways CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10) is an antioxidant produced by the body, essential for energy production in cells. Levels of CoQ10 naturally decrease with age…
Eggs: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Highlights Eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, containing all the essential vitamins and minerals needed for overall health. Vital role in a balanced diet, providing…
Iron Overload: Symptoms & Prevention Tips
Key Takeaways: Iron overload happens when the body absorbs excessive iron, which can damage organs. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, and skin changes. Early…
Red Palm Oil: Unveiling The Potent Health Benefits
Struggling to find the right oil for your health and kitchen? Red palm oil is packed with nutrients that might just be what you need….
Increase GLP-1 Agonists Naturally
Key Takeaways: GLP-1 agonists regulate appetite, insulin production, and blood sugar levels. Regular exercise and quality sleep maintain optimal GLP-1 levels. High-protein, low-carb diets effectively…
5 Major Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Key Takeaways Omega-3 fatty acids support heart health by reducing triglycerides and lowering blood pressure. They play an important role in brain function and development,…
Natural Treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Effective Remedies Explored
Understanding IBSSymptoms of IBSRole of Diet in IBSNatural Remedies for IBSSupplements for IBSRole of Probiotics in IBSFrequently Asked Questions Understanding IBS Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)…
Tallow: Benefits, Uses, and Nutrition
Key Takeaways: Tallow is a nutrient-rich animal fat with many practical uses. It contains valuable vitamins such as A, D, E, and K. Tallow is…
ALA vs. DHA & EPA Omega-3: Why Source Matters
Key Takeaways ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) is found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, but converts poorly to DHA and EPA. DHA and EPA are critical…
How Collagen Supports Healthy Skin, Joints, and More
Key Takeaways Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, supporting the structure of skin, bones, and connective tissues. It helps maintain skin elasticity,…
Protein: You probably need more
Key Takeaways Protein is needed for building and repairing body tissues. It supports muscle growth, immune function, and hormone production. Bioavailable sources of protein include…
Cholesterol Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways: High inflammation and blood pressure are major risk factors for heart disease. Cholesterol is vital for hormone production, cell membrane structure, and digestion,…
Boron: Benefits of a Lesser-Known Mineral
Key Takeaways Boron is a trace mineral with significant health benefits. It supports brain function, bone health, and hormonal balance. Understanding boron’s role can improve…
Silica: for Healthier Skin, Hair, and Nails
Key Takeaways: Silica supports strong and healthy skin, hair, and nails. It promotes bone health by boosting collagen production. Silica helps improve joint flexibility and…
11 Electrifying Health Benefits of Trace Minerals
What are Trace Minerals?The Major Roles of Trace MineralsSources of Trace MineralsDeficiencies in Trace MineralsThe Impact of Trace Minerals on Specific Health ConditionsFrequently Asked Questions…
Medium Chain Triglycerides (MCTs): Uncovering 5 Health Benefits
This potent, natural source of energy has gained considerable attention in recent years for its impressive array of benefits. MCT oil is a versatile addition…
How Cod Liver Oil Can Transform Your Health and Wellness
Cod liver oil has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various health conditions. Packed with essential nutrients and fatty acids, cod liver…
Magnesium: Better Sleep, Stress Relief and More
Taurine: The Mighty Amino Acid for Optimal Health
Key Takeaways Taurine supports heart health, regulates blood pressure, and reduces oxidative stress. Essential for muscle function, brain health, and cognitive function. Aids in insulin…
Spirulina: Health Benefits and Uses
Key Takeaways Spirulina boosts immune function with its high nutrient content and antioxidant properties. Rich in proteins and essential vitamins, enhances overall nutrition. Helps reduce…
Benefits of Nutritional Yeast
Key Takeaways Nutritional yeast is a rich source of vitamins and minerals. It supports immune function and promotes skin health. Its cheesy flavor makes it…
Potassium: Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways Potassium is essential for regulating fluid balance, nerve signals, and muscle function. It supports heart health and helps maintain proper blood pressure. Adequate…
Benefits of Sea Moss Explained
Key Takeaways Rich in Nutrients: Sea moss is packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting overall health and wellness. Supports Immune Function: Its high…
6 Best Natural Ways to Manage Your Blood Sugar: A Quick & Easy Guide
1. Intermittent fasting2. Exercise3. Dietary fiber4. Sleep5. Weight loss6. SupplementationBioclinic NaturalsPGX BiotiquestSugar Shift Every time you eat it, it’s plotting something sinister. Sugar isn’t as…
Healthy Fat: is Butter Better?
Key Takeaways Saturated fats, like those found in butter, may not be as harmful as once thought and can be part of a healthy diet….
Whole Food Vitamin C Complex: Expert Tips for Health
Key Highlights Whole food vitamin C complex is essential for a strong immune system and overall health. Unlike synthetic ascorbic acid, whole food vitamin C…
8 Key Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Key Takeaways Magnesium: A multitasker that aids in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. Copper: Supports neurological function, cardiovascular and immune system health, iron…
Vitamin A (Retinol): Essential Nutrient for Health
Key Takeaways: Natural Vitamin A, also known as Retinol, is crucial for vision, immune function, and skin health. Retinol is essential for healthy vision, particularly…
The Impact of Ultra-Processed Foods on Your Wellbeing
Every bite we take is a step toward either wellness or illness. In our fast-paced world, ultra-processed foods have become a staple, silently shaping our…
13 Most Dangerous Foods Revealed
Key Highlights Fugu, or pufferfish, is one of the most poisonous foods in the world, with its organs containing a neurotoxin that can paralyze motor…
5-HTP: Natural Ways to Boost Serotonin and Improve Mood
Key Takeaways: 5-HTP is a natural compound that helps boost serotonin levels in the brain. It can support mood regulation, sleep improvement, and stress reduction….
Keto Diet 101: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Key Highlights The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that can lead to weight loss and has many health benefits. By reducing carbohydrate intake…
L-Glutamine and Gut Health: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Glutamine is essential for gut health. Benefits include improved digestion and reduced inflammation. Potential side effects are rare but can occur in high…
Bee Pollen: Nature’s Secret Superfood
Key Takeaways Bee pollen is packed with essential nutrients and offers numerous health benefits. It supports immune function, boosts energy, and promotes overall well-being. Adding…
Do This! The Ultimate Guide to Fasting Safely and Effectively
In our increasingly busy lives, finding time to take care of our bodies can often take a backseat. One method that has gained attention recently…
Carnivore Diet: Benefits, Risks, Food List & More
Key Takeaways The carnivore diet is a keto diet that only allows for animal-based foods, and has potential health benefits. Tips for success include hydrating,…
What You Need to Know About Salt and Your Health
Table of ContentsThe Health Benefits of Unrefined Sea SaltElectrolyte BalanceMineral ContentImproved HydrationBoosted Energy LevelsImmune SupportImproved DigestionBalanced pH LevelsReduced Water RetentionHeart Health SupportStronger Bones and TeethEnhanced…
Copper: Little-Known Health Benefits
Key Takeaways Copper is an essential trace mineral with benefits, including ceruloplasmin production, energy production and antioxidant properties. Copper is critical for brain health by…
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA): Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways CLA is a type of fatty acid found primarily in animal products like beef and dairy. Known for potential benefits such as weight…
Trimethylglycine TMG: Betaine Anhydrous Explained
Key Takeaways Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) is a compound found naturally in various foods and offers several health benefits. TMG supports liver health by reducing fatty…
Calcium Supplements: What You Need to Know
Key Takeaways Calcium supplements have been linked to heart disease and kidney stones. Excess calcium from supplements can lead to imbalances and health issues. Natural…
Creatine Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways Common myths about creatine, such as it causing kidney damage, weight gain, and being a steroid, are widespread but unsupported by scientific evidence….
Berberine Has 11 More Incredible Benefits Than You Thought
Berberine is a compound found in several plants that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda. It has recently gained popularity…
Actual Superfoods: Real Foods You Should Be Eating
Key Takeaways Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods, offering essential vitamins, minerals, and fats. Prioritize high-quality sources for optimal nutrition. They support overall health, boost energy, and…
Grains & Legumes Secretly Harming Your Health? Find Out Now!
Key Takeaways: – Grains and legumes contain antinutrients like lectins and phytic acid, which can interfere with nutrient absorption. – These foods may trigger digestive…
13 Most Dangerous Foods Revealed
Key Highlights Fugu, or pufferfish, is one of the most poisonous foods in the world,…
Cholesterol Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways: High inflammation and blood pressure are major risk factors for heart disease. Cholesterol…
Minimalist Travel: Less Baggage, More Memories
Key Takeaways Learn to pack only essential items for any trip, keeping your luggage light….
Vitamin K2 and The Calcium Paradox by Kate Rheaume-Bleue
Key Takeaways Explains Vitamin K2’s role in calcium distribution. Links deficiency to bone and heart…
Natural Childbirth: Pain Management & Breathing
Key Takeaways Natural childbirth focuses on managing labor without medical interventions. Breathing techniques help alleviate…
Remnant Cholesterol (RC): Its Origins & Impact
Key Takeaways Remnant cholesterol (RC) is the cholesterol content left in the blood after triglycerides…
Anxiety: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Key Takeaways: Anxiety can disrupt daily life when it becomes overwhelming. Common symptoms include restlessness,…
Metabolic Health: What It Means and How to Improve It
Key Takeaways Metabolic health reflects how well your body processes energy and maintains stable blood…
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Key Takeaways GABA is a neurotransmitter that helps calm the nervous system. Low GABA levels…
Benefits of Sea Moss Explained
Key Takeaways Rich in Nutrients: Sea moss is packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants,…
Trimethylglycine TMG: Betaine Anhydrous Explained
Key Takeaways Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) is a compound found naturally in various foods and offers…