Key Takeaways
- Taurine supports heart health, regulates blood pressure, and reduces oxidative stress.
- Essential for muscle function, brain health, and cognitive function.
- Aids in insulin sensitivity, metabolic health, and liver detoxification.
- Found abundantly in animal-based foods like meat, fish, and dairy.
- Taurine supplements can enhance overall health, especially at 500mg daily.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Taurine is a powerful amino acid essential for optimal health. It plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, from heart health to muscle performance.
What is Taurine?
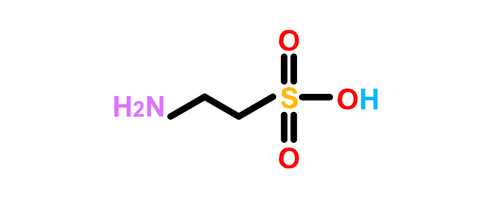
Taurine is a unique amino acid vital for many physiological processes. Unlike other amino acids, it isn’t used to build proteins.
Instead, taurine supports functions like bile salt formation, eye health, heart function, and the development of the nervous system.
Animal-based foods are rich sources of taurine, making them an important part of a balanced diet.
Health Benefits of Taurine
Cardiovascular Health

Taurine significantly impacts heart health. It helps regulate blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reduces oxidative stress, and protects the heart by modifying blood lipids.
Taurine’s ability to lower blood pressure is attributed to its role in vasodilation and inhibiting the production of angiotensin II.
Muscle Function and Athletic Performance
Taurine enhances muscle function and recovery. It increases calcium storage capacity, improves the sensitivity of force-generating proteins, promotes fat utilization, reduces glycogen use, and enhances mitochondrial function, making it beneficial for athletes and active individuals.
Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Taurine supplementation for prevention of stroke-like episodes in MELAS: a multicentre, open-label, 52-week phase III trial https://t.co/IEogTD6y0e
— Open Integrative (@openintegrative) June 8, 2024
Taurine supports brain health by regulating neurotransmitters and protecting against neurotoxicity.
Its antioxidant properties help scavenge free radicals and regulate antioxidant enzymes, contributing to improved cognitive function and mental clarity.
Eye Health
Taurine is crucial for maintaining retinal health. It helps protect the eyes from oxidative stress and supports overall visual function.
Taurine and Metabolic Health
Taurine positively affects insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, making it beneficial for managing diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
It also supports liver function and detoxification processes, playing a key role in metabolic health.
Immune System Support
Taurine supports the immune system by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. It modulates immune responses and helps maintain overall immune function, contributing to better health and disease prevention.
Dietary Sources of Taurine
Animal-based foods are the best sources of taurine. These include:
- Meat (beef, lamb, pork)
- Fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
Adding Taurine to Your Diet
Increasing taurine intake through diet is simple with these tips:
- Eat More Meat: Include beef, lamb, or pork in your meals.
- Enjoy Fish: Add salmon, mackerel, or sardines to your diet.
- Consume A2 Dairy: Add milk, cheese, or yogurt to your daily intake.
Heat Sensitivity
Taurine is relatively heat-stable but prolonged cooking times and high temperatures can lead to some degradation. The extent of taurine loss can vary depending on the cooking method.
Cooking Methods and Taurine Retention
- Boiling and Steaming: These methods can lead to some loss of taurine as it leaches into the cooking water. However, steaming tends to preserve more taurine compared to boiling.
- Baking and Roasting: Moderate loss of taurine can occur with these methods, especially if the cooking duration is long and temperatures are high.
- Frying: Deep frying can cause significant taurine loss due to the high temperatures involved.
- Grilling and Broiling: Similar to frying, these methods can result in substantial taurine loss because of the high direct heat.
To retain the most taurine in your food:
- Choose gentler cooking methods, such as steaming or baking at lower temperatures.
- Avoid prolonged cooking times to minimize nutrient loss.
- Consume cooking liquids, like broths or soups, when boiling meats, as taurine can leach into the liquid.
Taurine Supplements
Taurine supplements can be a convenient way to ensure adequate intake. Recommended dosages typically start at 500mg daily.
Country Life
Taurine
- Taurine is a vital amino acid found in the nervous system and muscles, essential for nerve activity.
- Vitamin B6 is added to improve taurine utilization.
- Ensures potency, from tested raw materials to final packaging.
- Uses pure, laboratory-tested ingredients to guarantee authenticity.
- Responsibly made: Gluten-free, vegan, kosher, and eco-friendly, supporting wind power and free from common allergens and additives.
Supplements are available in various forms, including capsules and powders. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to ensure it’s appropriate for your needs.
How Taurine Supports Overall Health
Liver Health & Detoxification
Taurine supports liver function and aids in detox processes, helping the body eliminate toxins efficiently.
Healthy Aging
Taurine promotes healthy aging by protecting cells from damage, supporting cognitive function, and maintaining physical health.
Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolism
Taurine improves insulin sensitivity, supports glucose metabolism, and aids in managing diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Electrolyte Balance and Immune Function
Taurine helps maintain electrolyte balance and modulates the immune system, contributing to overall health and disease prevention.
Taurine deficiency is a driver of aging, and, I know you'll be shocked, it's also a marker of poor metabolic health and obesity.
— P. D. Mangan Health & Freedom Maximalist 🇺🇸 (@Mangan150) January 14, 2024
Once more showing that staying lean and fit and eating right slows aging and leads to longer lifespan and healthspan. pic.twitter.com/Ey3yQmyYI5
Conclusion
Taurine is a vital amino acid with numerous health benefits. From supporting heart and brain health to enhancing athletic performance and metabolic function, taurine plays a crucial role in overall well-being. Including taurine-rich foods in your diet and considering supplements can help ensure you receive the full range of benefits this mighty amino acid offers.
FAQs
Does freezing food affect taurine content? Freezing food does not significantly affect taurine levels. The primary concern with taurine loss is during cooking, not storage.
Can I supplement taurine if I am worried about losing it through cooking? Yes, taurine supplements are available and can be an option if you are concerned about not getting enough through your diet.
Are there any plant-based sources of taurine? Taurine is primarily found in animal-based foods. Plant-based sources generally do not contain significant amounts of taurine, making it important for those on plant-based diets to consider supplementation.
Does microwaving food affect taurine levels? Microwaving can cause some taurine loss, but it is generally less than methods involving higher heat and longer cooking times.
How much taurine is recommended daily? While there is no established daily recommended intake for taurine, typical diets provide about 40-400 mg of taurine per day. For those considering supplementation, doses often range from 500-2000 mg per day, but it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider.
Research
Ahmadian, M., Dabidi Roshan, V., & Ashourpore, E. (2017). Taurine supplementation improves functional capacity, myocardial oxygen consumption, and electrical activity in heart failure. Journal of Dietary Supplements, 14(4), 422–432.
https://doi.org/10.1080/19390211.2016.1267059
Antonarakis, S. E. (2020). Taurine newborn screening to prevent one form of retinal degeneration and cardiomyopathy. European Journal of Human Genetics, 28(11), 1479–1480. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0671-3
Baliou, S., Adamaki, M., Ioannou, P., Pappa, A., Panayiotidis, M. I., Spandidos, D. A., …, & Zoumpourlis, V. (2021). Protective role of taurine against oxidative stress (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports, 24(2). https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12242
Bkaily, G., Jazzar, A., Normand, A., Simon, Y., Al-Khoury, J., & Jacques, D. (2020). Taurine and cardiac disease: State of the art and perspectives. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 98(2), 67–73. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2019-0313
Bouckenooghe, T., Remacle, C., & Reusens, B. (2006). Is taurine a functional nutrient? Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 9(6), 728–733. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mco.0000247469.26414.55
Caine, J. J., & Geracioti, T. D. (2016). Taurine, energy drinks, and neuroendocrine effects. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, 83(12), 895–904. htps://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.83a.15050
Castelli, V., Paladini, A., d'Angelo, M., Allegretti, M., Mantelli, F., Brandolini, L., …, & Varrassi, G. (2021). Taurine and oxidative stress in retinal health and disease. CNS Neuroscience and Therapeutics, 27(4), 403–412.
https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13610
Chaudhry, S., Tandon, B., Gupta, A., & Gupta, S. (2018). Taurine: A potential mediator for periodontal therapy. Indian Journal of Dental Research, 29(6), 808–811. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_123_17
Chawla, D. (2018). Taurine and neonatal nutrition. Indian Journal of Pediatrics, 85(10), 829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-018-2781-2
Chen, Q., Li, Z., Pinho, R. A., Gupta, R. C., Ugbolue, U. C., Thirupathi, A., & Gu, Y. (2021). The dose response of taurine on aerobic and strength exercises: A systematic review. Frontiers in Physiology, 12, 700352. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.700352
Chesney, R. W., Han, X., & Patters, A. B. (2010). Taurine and the renal system. Journal of Biomedical Science, 17(Suppl 1), S4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S4
Chung, M. C., Malatesta, P., Bosquesi, P. L., Yamasaki, P. R., Santos, J. L., & Vizioli, E. O. (2012). Advances in drug design based on the amino acid approach: Taurine analogues for the treatment of CNS diseases. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 5(10), 1128–1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5101128
Collin, C., Gautier, B., Gaillard, O., Hallegot, P., Chabane, S., Bastien, P., …, & Bernard, B. A. (2006). Protective effects of taurine on human hair follicle grown in vitro. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 28(4), 289–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2494.2006.00334.x
Colovic, M. B., Vasic, V. M., Djuric, D. M., & Krstic, D. Z. (2018). Sulphur-containing amino acids: Protective role against free radicals and heavy metals. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 25(3), 324–335. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170609075434
Curran, C. P., & Marczinski, C. A. (2017). Taurine, caffeine, and energy drinks: Reviewing the risks to the adolescent brain. Birth Defects Research, 109(20), 1640–1648. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdr2.1177
De Luca, A., Pierno, S., & Camerino, D. C. (2015). Taurine: The appeal of a safe amino acid for skeletal muscle disorders. Journal of Translational Medicine, 13, 243. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0610-1
Duchan, E., Patel, N. D., & Feucht, C. (2010). Energy drinks: A review of use and safety for athletes. The Physician and Sportsmedicine, 38(2), 171–179. https://doi.org/10.3810/psm.2010.06.1796
El Idrissi, A., Shen, C. H., & L'Amoreaux, W.J. (2013). Neuroprotective role of taurine during aging. Amino Acids, 45(4), 735–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1544-7
Froger, N., Moutsimilli, L., Cadetti, L., Jammoul, F., Wang, Q. P., Fan, Y., …, & Picaud, S. (2014). Taurine: The comeback of a neutraceutical in the prevention of retinal degenerations. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 41, 44–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.03.001
Guizoni, D. M., Freitas, I. N., Victorio, J. A., Possebom, I. R., Araujo, T. R., Carneiro, E. M., & Davel, A. P. (2021). Taurine treatment reverses protein malnutrition-induced endothelial dysfunction of the pancreatic vasculature: The role of hydrogen sulfide. Metabolism, 116, 154701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154701
Gutierrez-Hellin, J., & Varillas-Delgado, D. (2021). Energy drinks and sports performance, cardiovascular risk, and genetic associations; future prospects. Nutrients, 13(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030715
Han, X., & Chesney, R. W. (2012). The role of taurine in renal disorders. Amino Acids, 43(6), 2249–2263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1314-y
Heird, W. C. (2004). Taurine in neonatal nutrition--revisited. Archives of Disease in Childhood - Fetal and Neonatal Edition, 89(6), F473–474. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2004.055095
Inam, U. L., Piao, F., Aadil, R. M., Suleman, R., Li, K., Zhang, M., …, & Ahmed, Z. (2018). Ameliorative effects of taurine against diabetes: A review. Amino Acids, 50(5), 487–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2544-4
Ito, T., Schaffer, S., & Azuma, J. (2014). The effect of taurine on chronic heart failure: Actions of taurine against catecholamine and angiotensin II. Amino Acids, 46(1), 111–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1507-z
Jacobsen, J. G., & Smith, L. H. (1968). Biochemistry and physiology of taurine and taurine derivatives. Physiological Reviews, 48(2), 424–511. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1968.48.2.424
Jeong, J. S., & Choi, M. J. (2019). The intake of taurine and major food source of taurine in elementary school children in korea. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1155, 349–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8023-5_33
Jong, C. J., Azuma, J., & Schaffer, S. (2012). Mechanism underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: Prevention of mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids, 42(6), 2223–2232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0962-7
Jong, C. J., Sandal, P., & Schaffer, S. W. (2021). The role of taurine in mitochondria health: More than just an antioxidant. Molecules, 26(16). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164913
Joseph, G., Varughese, A., & Daniel, A. (2021). Determination of total proteinogenic amino acids and taurine by pre-column derivatization and UHPLC: Single laboratory validation, first action official method SM 2019.09. Journal of AOAC International, 104(2), 431–446. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsaa124
Kilb, W., & Fukuda, A. (2017). Taurine as an essential neuromodulator during perinatal cortical development. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 11, 328. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00328
Kurtz, J. A., VanDusseldorp, T. A., Doyle, J. A., & Otis, J. S. (2021). Taurine in sports and exercise. International Society of Sport Nutrition, 18(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-021-00438-0
Laidlaw, S. A., Grosvenor, M., & Kopple, J. D. (1990). The taurine content of common foodstuffs. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 14(2), 183–188. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607190014002183
Liu, C. L., Watson, A. M., Place, A. R., & Jagus, R. (2017). Taurine biosynthesis in a fish liver cell line (ZFL) adapted to a serum-free medium. Marine Drugs, 15(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060147
Lourenco, R., & Camilo, M. E. (2002). Taurine: A conditionally essential amino acid in humans? An overview in health and disease. Nutricion Hospitalaria, 17(6), 262–270
Marcinkiewicz, J., & Kontny, E. (2014). Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids, 46(1), 7–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1361-4
Mersman, B., Zaidi, W., Syed, N. I., & Xu, F. (2020). Taurine promotes neurite outgrowth and synapse development of both vertebrate and invertebrate central neurons. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience, 12, 29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2020.00029
Militante, J., & Lombardini, J. B. (2004). Age-related retinal degeneration in animal models of aging: Possible involvement of taurine deficiency and oxidative stress. Neurochemical Research, 29(1), 151–160. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:nere.0000010444.97959.1b
Miyazaki, T., Sasaki, S. I., Toyoda, A., Shirai, M., Ikegami, T., Matsuzaki, Y., & Honda, A. (2019). Influences of taurine deficiency on bile acids of the bile in the cat model. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1155, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8023-5_4
Mousavi, K., Niknahad, H., Ghalamfarsa, A., Mohammadi, H., Azarpira, N., Ommati, M. M., & Heidari, R. (2020). Taurine mitigates cirrhosis-associated heart injury through mitochondrial-dependent and antioxidative mechanisms. Clinical and Experimental Hepatology, 6(3), 207–219. https://doi.org/10.5114/ceh.2020.99513
Nakaya, Y., Minami, A., Harada, N., Sakamoto, S., Niwa, Y., & Ohnaka, M. (2000). Taurine improves insulin sensitivity in the Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rat, a model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 71(1), 54–58. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/71.1.54
National Library of Medicine (US). (2022). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 1123. Taurine | C2H7NO3S. PubChem. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Taurine
Rais, N., Ved, A., Ahmad, R., Parveen, K., & Mujeeb, M. (2021). In-vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic activity of the combined s-allyl cysteine and taurine. International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science, 12(11), 5747–5756. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.12(11).5747-56
Roysommuti, S., & Wyss, J. M. (2014). Perinatal taurine exposure affects adult arterial pressure control. Amino Acids, 46(1), 57–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1417-5
Schaffer, S., & Kim, H. W. (2018). Effects and mechanisms of taurine as a therapeutic agent. Biomolecules and Therapeutics (Seoul), 26(3), 225–241. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2017.251
Schaffer, S. W., Shimada, K., Jong, C. J., Ito, T., Azuma, J., & Takahashi, K. (2014). Effect of taurine and potential interactions with caffeine on cardiovascular function. Amino Acids, 46(5), 1147–1157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1708-0
Shao, A., & Hathcock, J. N. (2008). Risk assessment for the amino acids taurine, L-glutamine and L-arginine. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 50(3), 376–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2008.01.004
Sinha, M., Manna, P., & Sil, P. C. (2007). Taurine, a conditionally essential amino acid, ameliorates arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Toxicology in Vitro, 21(8), 1419–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2007.05.010
Spriet, L. L., & Whitfield, J. (2015). Taurine and skeletal muscle function. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 18(1), 96–101. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000135
Suarez, L. M., Munoz, M. D., Martin Del Rio, R., & Solis, J. M. (2016). Taurine content in different brain structures during ageing: Effect on hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Amino Acids, 48(5), 1199–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2155-2
Su, Y., Fan, W., Ma, Z., Wen, X., Wang, W., Wu, Q., & Huang, H. (2014). Taurine improves functional and histological outcomes and reduces inflammation in traumatic brain injury. Neuroscience, 266, 56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.006
Sun, Q., Wang, B., Li, Y., Sun, F., Li, P., Xia, W., …, & Zhu, Z. (2016). Taurine supplementation lowers blood pressure and improves vascular function in prehypertension: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Hypertension, 67(3), 541–549. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06624
Tao, X., Zhang, Z., Yang, Z., & Rao, B. (2022). The effects of taurine supplementation on diabetes mellitus in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Chemistry: Molecular Sciences, 4, 100106.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100106
Ueki, I., & Stipanuk, M. H. (2007). Enzymes of the taurine biosynthetic pathway are expressed in rat mammary gland. Journal of Nutrition, 137(8), 1887–1894. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/137.8.1887
Veeravalli, S., Phillips, I. R., Freire, R. T., Varshavi, D., Everett, J. R., & Shephard, E. A. (2020). Flavin-containing Monooxygenase 1 Catalyzes the production of taurine from hypotaurine. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 48(5), 378–385. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.119.089995
Wang, X., He, G., Mai, K., Xu, W., & Zhou, H. (2016). Differential regulation of taurine biosynthesis in rainbow trout and Japanese flounder. Scientific Reports, 6, 21231. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21231
Wu, G. (2020). Important roles of dietary taurine, creatine, carnosine, anserine and 4-hydroxyproline in human nutrition and health. Amino Acids, 52(3), 329–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-020-02823-6
Wu, G. F., Ren, S., Tang, R. Y., Xu, C., Zhou, J. Q., Lin, S. M., …, & Yang, J. C. (2017). Antidepressant effect of taurine in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive rats. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 4989. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05051-3
Yoshimura, T., Manabe, C., Inokuchi, Y., Mutou, C., Nagahama, T., & Murakami, S. (2021). Protective effect of taurine on UVB-induced skin aging in hairless mice. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 141, 111898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111898
Liver: 5 Surprising Benefits Backed by Science
Hold on! Don’t run away! You need to read this. Liver is a highly nutritious organ meat that is often overlooked in modern diets. Packed…
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA): Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways CLA is a type of fatty acid found primarily in animal products like beef and dairy. Known for potential benefits such as weight…
Magnesium: Better Sleep, Stress Relief and More
Vitamin A (Retinol): Essential Nutrient for Health
Key Takeaways: Natural Vitamin A, also known as Retinol, is crucial for vision, immune function, and skin health. Retinol is essential for healthy vision, particularly…
CoQ10: What Is It and Why Is It Important?
Key Takeaways CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10) is an antioxidant produced by the body, essential for energy production in cells. Levels of CoQ10 naturally decrease with age…
Cholesterol Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways: High inflammation and blood pressure are major risk factors for heart disease. Cholesterol is vital for hormone production, cell membrane structure, and digestion,…
Tallow: Benefits, Uses, and Nutrition
Key Takeaways: Tallow is a nutrient-rich animal fat with many practical uses. It contains valuable vitamins such as A, D, E, and K. Tallow is…
The Impact of Ultra-Processed Foods on Your Wellbeing
Every bite we take is a step toward either wellness or illness. In our fast-paced world, ultra-processed foods have become a staple, silently shaping our…
Protein: You probably need more
Key Takeaways Protein is needed for building and repairing body tissues. It supports muscle growth, immune function, and hormone production. Bioavailable sources of protein include…
L-Glutamine and Gut Health: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Glutamine is essential for gut health. Benefits include improved digestion and reduced inflammation. Potential side effects are rare but can occur in high…
How Stabilized Rice Bran Supports Digestive & Heart Health
Key Takeaways – Stabilized rice bran is a nutrient-rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. – The stabilization process prevents rancidity, making it a long-lasting…
Berberine Has 11 More Incredible Benefits Than You Thought
Berberine is a compound found in several plants that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda. It has recently gained popularity…
Do This! The Ultimate Guide to Fasting Safely and Effectively
In our increasingly busy lives, finding time to take care of our bodies can often take a backseat. One method that has gained attention recently…
Creatine Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways Common myths about creatine, such as it causing kidney damage, weight gain, and being a steroid, are widespread but unsupported by scientific evidence….
Grains & Legumes Secretly Harming Your Health? Find Out Now!
Key Takeaways: – Grains and legumes contain antinutrients like lectins and phytic acid, which can interfere with nutrient absorption. – These foods may trigger digestive…
How Cod Liver Oil Can Transform Your Health and Wellness
Cod liver oil has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various health conditions. Packed with essential nutrients and fatty acids, cod liver…
Trimethylglycine TMG: Betaine Anhydrous Explained
Key Takeaways Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) is a compound found naturally in various foods and offers several health benefits. TMG supports liver health by reducing fatty…
Whole Food Vitamin C Complex: Expert Tips for Health
Key Highlights Whole food vitamin C complex is essential for a strong immune system and overall health. Unlike synthetic ascorbic acid, whole food vitamin C…
6 Best Natural Ways to Manage Your Blood Sugar: A Quick & Easy Guide
1. Intermittent fasting2. Exercise3. Dietary fiber4. Sleep5. Weight loss6. SupplementationBioclinic NaturalsPGX BiotiquestSugar Shift Every time you eat it, it’s plotting something sinister. Sugar isn’t as…
Postbiotics: What They Are and Why They Are Important
Key Takeaways Postbiotics 101: They’re beneficial by-products from probiotics that consume prebiotics Boosts Immunity: Postbiotics sharpen your immune system, helping fight off pathogens and reducing…
Allulose: The Best Sugar Alternative
Key Takeaways Allulose is a low-calorie sweetener found naturally in some fruits. It does not raise blood sugar levels, making it suitable for diabetics. Allulose…
Copper: Little-Known Health Benefits
Key Takeaways Copper is an essential trace mineral with benefits, including ceruloplasmin production, energy production and antioxidant properties. Copper is critical for brain health by…
5-HTP: Natural Ways to Boost Serotonin and Improve Mood
Key Takeaways: 5-HTP is a natural compound that helps boost serotonin levels in the brain. It can support mood regulation, sleep improvement, and stress reduction….
How Collagen Supports Healthy Skin, Joints, and More
Key Takeaways Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, supporting the structure of skin, bones, and connective tissues. It helps maintain skin elasticity,…
Vitamin E Complex
Key Takeaways Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. The vitamin E complex includes…
Medium Chain Triglycerides (MCTs): Uncovering 5 Health Benefits
This potent, natural source of energy has gained considerable attention in recent years for its impressive array of benefits. MCT oil is a versatile addition…
Zinc Supplements: Risks and Dangers
Key Takeaways Zinc supports immunity, wound healing, and cell growth. High zinc supplement doses can cause health problems. Always consult a healthcare provider before taking…
Eggs: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Highlights Eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, containing all the essential vitamins and minerals needed for overall health. Vital role in a balanced diet, providing…
Calcium Supplements: What You Need to Know
Key Takeaways Calcium supplements have been linked to heart disease and kidney stones. Excess calcium from supplements can lead to imbalances and health issues. Natural…
Actual Superfoods: Real Foods You Should Be Eating
Key Takeaways Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods, offering essential vitamins, minerals, and fats. Prioritize high-quality sources for optimal nutrition. They support overall health, boost energy, and…
Increase GLP-1 Agonists Naturally
Key Takeaways: GLP-1 agonists regulate appetite, insulin production, and blood sugar levels. Regular exercise and quality sleep maintain optimal GLP-1 levels. High-protein, low-carb diets effectively…
Potassium: Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways Potassium is essential for regulating fluid balance, nerve signals, and muscle function. It supports heart health and helps maintain proper blood pressure. Adequate…
Silica: for Healthier Skin, Hair, and Nails
Key Takeaways: Silica supports strong and healthy skin, hair, and nails. It promotes bone health by boosting collagen production. Silica helps improve joint flexibility and…
Carnivore Diet: Benefits, Risks, Food List & More
Key Takeaways The carnivore diet is a keto diet that only allows for animal-based foods, and has potential health benefits. Tips for success include hydrating,…
Is Eating Sugar Really That Bad For Your Health?
Should You Really Be Concerned? In short, YES! Thank you, that’s all folks, and do have a good evening. Seriously though, extensive research has established…
What You Need to Know About Salt and Your Health
Table of ContentsThe Health Benefits of Unrefined Sea SaltElectrolyte BalanceMineral ContentImproved HydrationBoosted Energy LevelsImmune SupportImproved DigestionBalanced pH LevelsReduced Water RetentionHeart Health SupportStronger Bones and TeethEnhanced…
TUDCA Benefits for Health
Key Takeaways TUDCA promotes liver health, aiding cell protection and repair. Enhances digestion by improving bile flow and supporting gut health. May protect brain health…
Red Palm Oil: Unveiling The Potent Health Benefits
Struggling to find the right oil for your health and kitchen? Red palm oil is packed with nutrients that might just be what you need….
5 Major Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Key Takeaways Omega-3 fatty acids support heart health by reducing triglycerides and lowering blood pressure. They play an important role in brain function and development,…
ALA vs. DHA & EPA Omega-3: Why Source Matters
Key Takeaways ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) is found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, but converts poorly to DHA and EPA. DHA and EPA are critical…
Keto Diet 101: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Key Highlights The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that can lead to weight loss and has many health benefits. By reducing carbohydrate intake…
L-Carnitine: Benefits, Dosage, and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Carnitine supports fat metabolism and energy production. Benefits include enhanced exercise performance and improved heart health. Proper dosing minimizes potential side effects. Understanding…
Natural Treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Effective Remedies Explored
Understanding IBSSymptoms of IBSRole of Diet in IBSNatural Remedies for IBSSupplements for IBSRole of Probiotics in IBSFrequently Asked Questions Understanding IBS Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)…
13 Most Dangerous Foods Revealed
Key Highlights Fugu, or pufferfish, is one of the most poisonous foods in the world, with its organs containing a neurotoxin that can paralyze motor…
Bee Pollen: Nature’s Secret Superfood
Key Takeaways Bee pollen is packed with essential nutrients and offers numerous health benefits. It supports immune function, boosts energy, and promotes overall well-being. Adding…
Benefits of Sea Moss Explained
Key Takeaways Rich in Nutrients: Sea moss is packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting overall health and wellness. Supports Immune Function: Its high…
Spirulina: Health Benefits and Uses
Key Takeaways Spirulina boosts immune function with its high nutrient content and antioxidant properties. Rich in proteins and essential vitamins, enhances overall nutrition. Helps reduce…
Iron Overload: Symptoms & Prevention Tips
Key Takeaways: Iron overload happens when the body absorbs excessive iron, which can damage organs. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, and skin changes. Early…
Boron: Benefits of a Lesser-Known Mineral
Key Takeaways Boron is a trace mineral with significant health benefits. It supports brain function, bone health, and hormonal balance. Understanding boron’s role can improve…
Benefits of Nutritional Yeast
Key Takeaways Nutritional yeast is a rich source of vitamins and minerals. It supports immune function and promotes skin health. Its cheesy flavor makes it…
8 Key Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Key Takeaways Magnesium: A multitasker that aids in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. Copper: Supports neurological function, cardiovascular and immune system health, iron…
11 Electrifying Health Benefits of Trace Minerals
What are Trace Minerals?The Major Roles of Trace MineralsSources of Trace MineralsDeficiencies in Trace MineralsThe Impact of Trace Minerals on Specific Health ConditionsFrequently Asked Questions…
Healthy Fat: is Butter Better?
Key Takeaways Saturated fats, like those found in butter, may not be as harmful as once thought and can be part of a healthy diet….