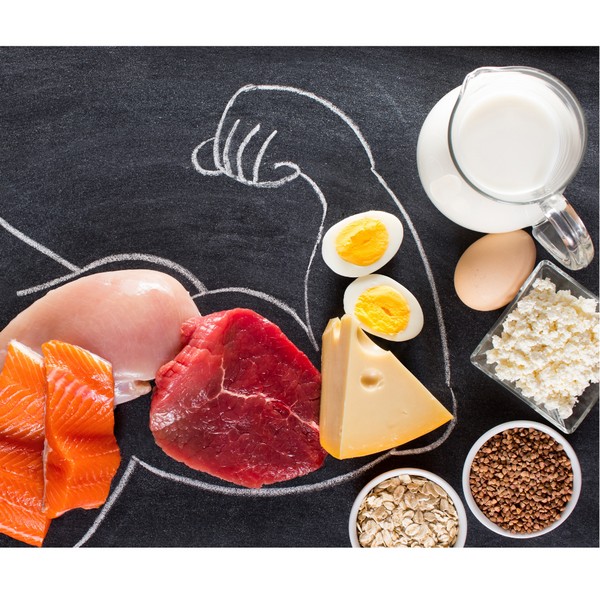
Hold on! Don’t run away! You need to read this. Liver is a highly nutritious organ meat that is often overlooked in modern diets. Packed with bioavailable copper, vitamins A, B12, B6, minerals like iron, zinc, and selenium, protein, and fatty acids, offering an array of health benefits.
Key Takeaways:
- It turns out your grandmother was right all along
- Liver is a nutritious organ meat packed with bioavailable copper, essential vitamins, minerals, protein, and fatty acids.
- Eating liver can promote brain health, boost immune system, treat anemia, support healthy vision, and aid in detoxification.
Table of Contents
What is The Nutritional Content Of Liver?
Liver is a nutrient-dense food rich in essential vitamins, minerals, protein, and healthy fats. It is particularly noted for its high levels of bioavailable Vitamin A (Retinol), which is important for maintaining healthy vision, as well as B vitamins, including B12 and folate, essential for energy production and red blood cell formation.
With its abundance of high-quality proteins and beneficial fatty acids like omega-3s, liver is a valuable dietary component for overall health and wellbeing.
Vitamins (A, B12, B6)
Liver is a powerhouse of essential vitamins such as vitamin A, B12, and B6, crucial for various bodily functions and health.
| Vitamin A | Plays a vital role in maintaining good vision, skin health, and a strong immune system. It also aids in cell growth and differentiation. |
| Vitamin B12 | Crucial for red blood cell formation and neurological function. Deficiency in B12 can lead to fatigue, weakness, and nerve damage. |
| Vitamin B6 | Contributes to protein metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis. It also supports immune function and helps in the production of red blood cells. These vitamins collectively optimize metabolism, boost immunity, and promote overall well-being. |
Minerals
Liver is a rich source of minerals including copper, zinc, and selenium, vital for various physiological processes and overall well-being.
| Copper | Essential for enzymatic reactions within the body, aiding in the formation of red blood cells, maintaining healthy nerve function, and supporting the immune system. Copper is also involved in the production of collagen, a protein essential for the health of connective tissues, skin, and bones. |
| Zinc | Required for immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. It also supports normal growth and development. |
| Selenium | Acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage and supporting the immune system. |
| Iron | Needed for oxygen transport in the body |
Combined, these minerals found in the liver contribute to a healthy metabolism, strong immunity, and efficient antioxidant functions. Including liver in the diet can help maintain optimal levels of these essential minerals, promoting overall health and well-being.
Protein
If you don't eat protein, you die.
— 💯 Sama Hoole 💯 (@SamaHoole) April 6, 2024
If you don't eat fat, you die.
If you don't eat carbs, you thrive.
Liver is a valuable source of high-quality protein necessary for tissue repair, muscle growth, and overall health.
This nutrient-dense organ meat is rich in essential amino acids like glutamine and carnitine, which play vital roles in protein synthesis and maintaining proper immune function. The protein found in liver is highly bioavailable, meaning the body can easily absorb and utilize it efficiently.
This makes liver an excellent choice for those looking to boost their protein intake in a natural and wholesome way. Regular consumption of liver can aid in supporting enzyme production, enhancing metabolic processes, and promoting optimal muscle repair and growth.
Fatty Acids
Liver contains essential fatty acids that support brain function, hormone production, and cardiovascular health. These fatty acids play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
For example, omega-3 fatty acids found in liver are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease.
In addition, the fatty acids in liver are essential for proper brain function, as they are key components of cell membranes and play a role in neurotransmitter function.
They also support hormonal balance, aiding in the production of important hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
Consuming liver regularly can be a great way to ensure an adequate intake of these essential fats, promoting optimal brain health, hormonal balance, and heart health.
What Are The Health Benefits Of Eating Liver?

Eating liver brings numerous health advantages, thanks to its rich content of vitamins, minerals, proteins, and fats. It’s especially high in vitamin A, which supports brain health, enhancing cognitive functions and memory.
Liver’s abundant iron prevents anemia and ensures healthy blood flow. With antioxidants such as copper and zinc, it strengthens the immune system and aids in fighting off infections.
Zinc also helps in keeping vision sharp. Additionally, liver aids in detoxification, boosting overall health. Including liver in your diet can significantly contribute to balanced nutrition and well-being.
Promotes Brain Health
Eating liver boosts brain health through essential fatty acids, like Omega-3 and Omega-6, which are pivotal for cognitive function and neurological health. These fatty acids improve problem-solving, decision-making, and focus.
Liver consumption is also associated with better memory and mental clarity, as its nutrients support brain function and protect neurological pathways.
Adding liver to your diet is a tasty strategy to provide your brain with essential nutrients for its best performance and enduring health.
Boosts Immune System
Liver’s nutrients significantly strengthen the immune system, aiding the body in combating infections for better overall health. Vitamin A in liver regulates immune responses and aids in the development of immune cells.
Its vitamin C content, a potent antioxidant, safeguards immune cells and boosts immunity.
Additionally, minerals like iron and zinc support antibody production and immune cell function. Liver proteins, rich in essential amino acids, serve as building blocks for antibodies and immune cells, underpinning a strong immune response.
Including liver in your diet ensures access to these critical nutrients, enhancing your body’s defense mechanisms.
Supports Healthy Vision
Liver, rich in vitamin A, significantly supports eye health and wards off vision issues. This nutrient, vital for eye health, acts as an antioxidant to shield the eyes from oxidative stress and free radical damage.
Crucially, it maintains retina health, pivotal for sharp vision. Vitamin A’s role in forming rhodopsin, a pigment in the retina’s rods, boosts night vision by aiding the eyes’ adjustment to dim light, highlighting its importance in a diet for optimal eye function and night vision enhancement.
Aids in Detoxification
The antioxidants in liver boost the body’s detoxification efforts, aiding in the removal of toxins and enhancing metabolic health. They neutralize toxins, fight oxidative stress, and guard against free radical damage, supporting the liver’s detox pathways.
This process is essential for breaking down and eliminating harmful substances, ensuring metabolic processes run smoothly.
Additionally, these antioxidants help in cell regeneration and repair, contributing to overall health and longevity. Including antioxidant-rich liver in your diet can amplify detoxification and assist your liver’s crucial roles.
Treatment of Anemia
In 1934, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to George R. Minot, William P. Murphy, and George H. Whipple. Their groundbreaking work centered around liver therapy in anemias .
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1934. NobelPrize.org. Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2024. Wed. 13 Mar 2024. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/1934/summary/
Liver consumption can help alleviate anemia by providing a rich source of bioavailable copper and B vitamins essential for proper iron regulation, red blood cell production and oxygen transport.
Liver Therapy in Anemia:
The groundbreaking discovery that led to the Nobel Prize involved the use of liver extracts to treat anemia. Whipple and his colleagues demonstrated that liver extracts could effectively treat anemia, particularly pernicious anemia.
Their research showed that liver therapy led to significant improvements in blood regeneration. Liver extracts contained essential factors that supported red blood cell production and helped combat anemia.
This breakthrough had a profound impact on medical practice and paved the way for further advancements in treating anemia.
Legacy and Impact:
Whipple’s work not only contributed to our understanding of anemia but also highlighted the critical role of the liver in maintaining blood health. His research laid the groundwork for subsequent studies on anemia and other blood disorders.
The Nobel Prize recognized the immense significance of liver therapy and its potential to save lives by addressing severe anemias.
How To Incorporate Liver Into Your Diet?
Try liver stir-fried with veggies or mixed into pasta for a protein boost. Liver tacos or liver curry bring exciting cultural tastes to your table, blending classic and contemporary styles.
Appetizers like liver bruschetta or liver skewers showcase liver’s versatility across various cuisines, making it a delightful addition to any culinary repertoire.
Liver Pate
Liver pate is a classic and luxurious dish that combines the rich flavors of liver with aromatic herbs and spices, perfect for spreading on toast or crackers.
When preparing liver pate, it’s essential to start with high-quality liver, such as chicken or duck liver, for a creamy and flavorful result. The liver is typically pan-seared with shallots, garlic, and butter until cooked through but still pink inside, ensuring a tender texture.
- After blending the cooked liver mixture with cream, eggs, and seasonings in a food processor, it is then chilled to allow the flavors to meld together.
Liver and Onions
Liver and onions is a hearty and savory dish that combines the rich flavors of liver with caramelized onions, creating a delicious meal packed with nutrients.
When preparing liver and onions, it is essential to ensure that the liver is properly cleaned and trimmed to remove any excess fat or membranes. This process not only enhances the texture of the dish but also helps eliminate any potential bitterness that some may find off-putting.
The key to achieving a perfect balance of flavors lies in cooking the liver till it is just cooked through, resulting in a tender and velvety texture. Pairing the liver with sweet caramelized onions adds a delightful contrast of flavors, with the natural sweetness of the onions complementing the richness of the liver impeccably.
Liver Stir-Fry
Liver stir-fry is a quick and flavorful way to enjoy the nutritional benefits of liver, combining tender slices of liver with fresh vegetables and savory sauces.
When making liver stir-fry, selecting the right liver is crucial for a successful outcome. Opt for high-quality liver from a reputable source to ensure freshness and optimal taste. Common choices include chicken liver, beef liver, or pork liver, each offering its unique flavor profile.
Cutting the liver into thin slices against the grain helps to tenderize it and allows for quick cooking. Pairing the liver with an assortment of colorful vegetables such as bell peppers, onions, and mushrooms not only enhances the visual appeal but also adds a variety of textures and tastes.
Liver Smoothie
Liver smoothie is a unique and nutrient-packed beverage that blends liver with fruits, vegetables, and superfoods to create a healthful and refreshing drink.
These smoothies offer a convenient and delicious way to incorporate nutrient-dense organ meat into your diet. The addition of liver brings a rich source of iron, B vitamins, and essential minerals, enhancing the nutritional profile of the smoothie. By combining liver with ingredients like spinach, berries, or avocados, you can mask the strong flavor of the organ meat while introducing a variety of flavors and textures to your drink.
Dessicated Beef Liver Capsules
For those who just for some reason can’t or won’t try eating liver, there is an alternative option in the form of supplements.

How Much Liver Should Be Consumed?
The recommended amount of liver consumption varies depending on individual health conditions, dietary preferences, and nutrient needs.
It is essential to consider your personal health status and any existing dietary requirements before incorporating liver into your meals.
- Overconsumption of liver can lead to an intake of excessive amounts of certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A and copper.
- Therefore, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist to determine the appropriate amount of liver that aligns with your nutritional goals.
It’s beneficial to source high-quality, organically raised liver to ensure you are getting the best nutritional benefits.
Incorporating liver into your meals can be both delicious and inventive, from traditional liver pâté to inventive liver smoothies.
Conclusion
Liver offers a unique blend of health benefits and risks, making it a food choice that requires moderation and balance in dietary planning. Rich in essential nutrients such as iron, Vitamin A, B vitamins, and protein, liver plays a crucial role in supporting overall health.
Despite its nutritional value, excessive consumption of liver can lead to high intake of vitamin A, posing potential health risks. It is advisable to incorporate liver in moderation to reap its benefits without exceeding daily nutrient limits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the nutritional content of liver?
Liver is known to be a superfood due to its high nutritional content. It is rich in bioavailable copper, vitamins, minerals, protein, and fatty acids.
How much copper is found in liver?
Liver is an excellent source of copper, containing about 12.7 mg per 100 grams of liver. This essential mineral is important for maintaining a healthy immune system and aiding in the production of red blood cells.
What vitamins can be found in liver?
Liver is a great source of vitamins A, B12, and D. These vitamins play important roles in maintaining eye health, supporting nerve function, and strengthening bones, respectively.
Is liver a good source of minerals?
Yes, liver is a great source of minerals such as iron, zinc, and phosphorus. These minerals are important for various bodily functions, including oxygen transport, immune system function, and bone health.
Why is liver a good source of protein?
Liver is a rich source of high-quality protein, containing essential amino acids necessary for building and repairing tissues in the body. This makes it a great food choice for those looking to increase their protein intake.
What are the health benefits of eating liver?
Eating liver has numerous health benefits, including improved energy levels, boosted immune system, healthier skin and hair, and better cognitive function. Its high nutrient content also makes it beneficial for preventing nutrient deficiencies.
Research
Ortiz-Hidalgo C. George H. Whipple. Premio Nobel en Fisiología y Medicina en 1934. La enfermedad de Whipple, la anemia perniciosa y otras contribuciones a la medicina [George H. Whipple. Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1934. Whipple's disease, pernicious anemia, and other contributions to medicine]. Gac Med Mex. 2002 Jul-Aug;138(4):371-6. Spanish. PMID: 12200882.
https://www.medigraphic.com/cgi-bin/new/resumen.cgi?IDARTICULO=7472
MEYER LM, RITZ ND, et al. Studies in pernicious anemia patients treated with liver extract and folic acid antagonists. Am J Med Sci. 1949 Aug;218(2):197-203. PMID: 18147209.
doi: 10.1097/00000441-194908000-00012
KOTHARI BV, BHENDE YM. Crude liver extract, refined liver extract and folic acid in the treatment of pernicious anaemia of pregnancy. Indian J Med Res. 1950 Oct;38(4):385-92. PMID: 14840873.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14840873/
MOLLIN DL. Treatment of pernicious anaemia with parenteral liver extract; a review of 51 patients between 1940 and 1948. Lancet. 1950 Jun 10;1(6615):1064-8. PMID: 15422820.444.
doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(50)90902-0
Jeney A. Az anaemia perniciosa terápiájának története [History of the therapy of pernicious anemia]. Orv Hetil. 2013 Nov 3;154(44):1754-8. Hungarian. doi: 10.1556/OH.2013.29743. PMID: 24161600.
FOUTS PJ, ZERFAS LG. LIVER-GASTRIC TISSUE PREPARATIONS IN THE TREATMENT OF PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. JAMA. 1933;101(3):188–192. doi:10.1001/jama.1933.02740280008004
Isaacs R, Bethell FH, Riddle MC, Friedman A. STANDARDS FOR RED BLOOD CELL INCREASE AFTER LIVER AND STOMACH THERAPY IN PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. JAMA. 1938;111(25):2291. doi:10.1001/jama.1938.72790510002011a
Whipple, G.H., Robscheit, F.S. and Hooper, C.W., 1920. Blood regeneration following simple anemia: IV. Influence of meat, liver and various extractives, alone or combined with standard diets. American Journal of Physiology-Legacy Content, 53(2), pp.236-262.
Shen, R., Yang, D., Zhang, L., Yu, Q., Ma, X., Ma, G., Guo, Z., & Chen, C. Preparation of Complementary Food for Infants and Young Children with Beef Liver: Process Optimization and Storage Quality. Foods, 12(14), 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142689
Estevez, M.; Ventanas, J.; Cava, R.; Puolanne, E. Characterisation of a traditional Finnish liver sausage and different types of Spanish liver pates: A comparative study. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 657–669.
Victor A. Hoffbrand. THE DISCOVERY OF THE CURE FOR PERNICIOUS ANAEMIA, VITAMIN B12 Nobel Prizes that Changed Medicine. December 2011, 21-43
Taurine: The Mighty Amino Acid for Optimal Health
Key Takeaways Taurine supports heart health, regulates blood pressure, and reduces oxidative stress. Essential for muscle function, brain health, and cognitive function. Aids in insulin…
8 Key Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Key Takeaways Magnesium: A multitasker that aids in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. Copper: Supports neurological function, cardiovascular and immune system health, iron…
Berberine Has 11 More Incredible Benefits Than You Thought
Berberine is a compound found in several plants that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda. It has recently gained popularity…
Iron Overload: Symptoms & Prevention Tips
Key Takeaways: Iron overload happens when the body absorbs excessive iron, which can damage organs. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, and skin changes. Early…
How Cod Liver Oil Can Transform Your Health and Wellness
Cod liver oil has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various health conditions. Packed with essential nutrients and fatty acids, cod liver…
Eggs: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Highlights Eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, containing all the essential vitamins and minerals needed for overall health. Vital role in a balanced diet, providing…
Vitamin E Complex
Key Takeaways Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. The vitamin E complex includes…
Medium Chain Triglycerides (MCTs): Uncovering 5 Health Benefits
This potent, natural source of energy has gained considerable attention in recent years for its impressive array of benefits. MCT oil is a versatile addition…
Magnesium: Better Sleep, Stress Relief and More
Zinc Supplements: Risks and Dangers
Key Takeaways Zinc supports immunity, wound healing, and cell growth. High zinc supplement doses can cause health problems. Always consult a healthcare provider before taking…
Grains & Legumes Secretly Harming Your Health? Find Out Now!
Key Takeaways: – Grains and legumes contain antinutrients like lectins and phytic acid, which can interfere with nutrient absorption. – These foods may trigger digestive…
Healthy Fat: is Butter Better?
Key Takeaways Saturated fats, like those found in butter, may not be as harmful as once thought and can be part of a healthy diet….
Actual Superfoods: Real Foods You Should Be Eating
Key Takeaways Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods, offering essential vitamins, minerals, and fats. Prioritize high-quality sources for optimal nutrition. They support overall health, boost energy, and…
Creatine Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways Common myths about creatine, such as it causing kidney damage, weight gain, and being a steroid, are widespread but unsupported by scientific evidence….
Postbiotics: What They Are and Why They Are Important
Key Takeaways Postbiotics 101: They’re beneficial by-products from probiotics that consume prebiotics Boosts Immunity: Postbiotics sharpen your immune system, helping fight off pathogens and reducing…
Vitamin A (Retinol): Essential Nutrient for Health
Key Takeaways: Natural Vitamin A, also known as Retinol, is crucial for vision, immune function, and skin health. Retinol is essential for healthy vision, particularly…
Calcium Supplements: What You Need to Know
Key Takeaways Calcium supplements have been linked to heart disease and kidney stones. Excess calcium from supplements can lead to imbalances and health issues. Natural…
What You Need to Know About Salt and Your Health
Table of ContentsThe Health Benefits of Unrefined Sea SaltElectrolyte BalanceMineral ContentImproved HydrationBoosted Energy LevelsImmune SupportImproved DigestionBalanced pH LevelsReduced Water RetentionHeart Health SupportStronger Bones and TeethEnhanced…
Potassium: Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways Potassium is essential for regulating fluid balance, nerve signals, and muscle function. It supports heart health and helps maintain proper blood pressure. Adequate…
5 Major Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Key Takeaways Omega-3 fatty acids support heart health by reducing triglycerides and lowering blood pressure. They play an important role in brain function and development,…
Is Eating Sugar Really That Bad For Your Health?
Should You Really Be Concerned? In short, YES! Thank you, that’s all folks, and do have a good evening. Seriously though, extensive research has established…
Benefits of Sea Moss Explained
Key Takeaways Rich in Nutrients: Sea moss is packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting overall health and wellness. Supports Immune Function: Its high…
6 Best Natural Ways to Manage Your Blood Sugar: A Quick & Easy Guide
1. Intermittent fasting2. Exercise3. Dietary fiber4. Sleep5. Weight loss6. SupplementationBioclinic NaturalsPGX BiotiquestSugar Shift Every time you eat it, it’s plotting something sinister. Sugar isn’t as…
CoQ10: What Is It and Why Is It Important?
Key Takeaways CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10) is an antioxidant produced by the body, essential for energy production in cells. Levels of CoQ10 naturally decrease with age…
How Stabilized Rice Bran Supports Digestive & Heart Health
Key Takeaways – Stabilized rice bran is a nutrient-rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. – The stabilization process prevents rancidity, making it a long-lasting…
Copper: Little-Known Health Benefits
Key Takeaways Copper is an essential trace mineral with benefits, including ceruloplasmin production, energy production and antioxidant properties. Copper is critical for brain health by…
Whole Food Vitamin C Complex: Expert Tips for Health
Key Highlights Whole food vitamin C complex is essential for a strong immune system and overall health. Unlike synthetic ascorbic acid, whole food vitamin C…
The Impact of Ultra-Processed Foods on Your Wellbeing
Every bite we take is a step toward either wellness or illness. In our fast-paced world, ultra-processed foods have become a staple, silently shaping our…
Silica: for Healthier Skin, Hair, and Nails
Key Takeaways: Silica supports strong and healthy skin, hair, and nails. It promotes bone health by boosting collagen production. Silica helps improve joint flexibility and…
Red Palm Oil: Unveiling The Potent Health Benefits
Struggling to find the right oil for your health and kitchen? Red palm oil is packed with nutrients that might just be what you need….
11 Electrifying Health Benefits of Trace Minerals
What are Trace Minerals?The Major Roles of Trace MineralsSources of Trace MineralsDeficiencies in Trace MineralsThe Impact of Trace Minerals on Specific Health ConditionsFrequently Asked Questions…
L-Glutamine and Gut Health: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Glutamine is essential for gut health. Benefits include improved digestion and reduced inflammation. Potential side effects are rare but can occur in high…
Natural Treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Effective Remedies Explored
Understanding IBSSymptoms of IBSRole of Diet in IBSNatural Remedies for IBSSupplements for IBSRole of Probiotics in IBSFrequently Asked Questions Understanding IBS Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)…
Bee Pollen: Nature’s Secret Superfood
Key Takeaways Bee pollen is packed with essential nutrients and offers numerous health benefits. It supports immune function, boosts energy, and promotes overall well-being. Adding…
How Collagen Supports Healthy Skin, Joints, and More
Key Takeaways Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, supporting the structure of skin, bones, and connective tissues. It helps maintain skin elasticity,…
Allulose: The Best Sugar Alternative
Key Takeaways Allulose is a low-calorie sweetener found naturally in some fruits. It does not raise blood sugar levels, making it suitable for diabetics. Allulose…
Protein: You probably need more
Key Takeaways Protein is needed for building and repairing body tissues. It supports muscle growth, immune function, and hormone production. Bioavailable sources of protein include…
Do This! The Ultimate Guide to Fasting Safely and Effectively
In our increasingly busy lives, finding time to take care of our bodies can often take a backseat. One method that has gained attention recently…
Carnivore Diet: Benefits, Risks, Food List & More
Key Takeaways The carnivore diet is a keto diet that only allows for animal-based foods, and has potential health benefits. Tips for success include hydrating,…
Spirulina: Health Benefits and Uses
Key Takeaways Spirulina boosts immune function with its high nutrient content and antioxidant properties. Rich in proteins and essential vitamins, enhances overall nutrition. Helps reduce…
Boron: Benefits of a Lesser-Known Mineral
Key Takeaways Boron is a trace mineral with significant health benefits. It supports brain function, bone health, and hormonal balance. Understanding boron’s role can improve…
Benefits of Nutritional Yeast
Key Takeaways Nutritional yeast is a rich source of vitamins and minerals. It supports immune function and promotes skin health. Its cheesy flavor makes it…
ALA vs. DHA & EPA Omega-3: Why Source Matters
Key Takeaways ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) is found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, but converts poorly to DHA and EPA. DHA and EPA are critical…
13 Most Dangerous Foods Revealed
Key Highlights Fugu, or pufferfish, is one of the most poisonous foods in the world, with its organs containing a neurotoxin that can paralyze motor…
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA): Benefits & Sources
Key Takeaways CLA is a type of fatty acid found primarily in animal products like beef and dairy. Known for potential benefits such as weight…
Trimethylglycine TMG: Betaine Anhydrous Explained
Key Takeaways Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) is a compound found naturally in various foods and offers several health benefits. TMG supports liver health by reducing fatty…
5-HTP: Natural Ways to Boost Serotonin and Improve Mood
Key Takeaways: 5-HTP is a natural compound that helps boost serotonin levels in the brain. It can support mood regulation, sleep improvement, and stress reduction….
TUDCA Benefits for Health
Key Takeaways TUDCA promotes liver health, aiding cell protection and repair. Enhances digestion by improving bile flow and supporting gut health. May protect brain health…
Keto Diet 101: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Key Highlights The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that can lead to weight loss and has many health benefits. By reducing carbohydrate intake…
Tallow: Benefits, Uses, and Nutrition
Key Takeaways: Tallow is a nutrient-rich animal fat with many practical uses. It contains valuable vitamins such as A, D, E, and K. Tallow is…
Cholesterol Misconceptions: Separating Fact from Fiction
Key Takeaways: High inflammation and blood pressure are major risk factors for heart disease. Cholesterol is vital for hormone production, cell membrane structure, and digestion,…
L-Carnitine: Benefits, Dosage, and Side Effects
Key Takeaways L-Carnitine supports fat metabolism and energy production. Benefits include enhanced exercise performance and improved heart health. Proper dosing minimizes potential side effects. Understanding…